Erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a case report
- PMID: 30288093
- PMCID: PMC6163005
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S164489
Erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a case report
Abstract
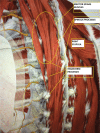
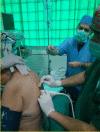
The Erector Spinae Plane Block (ESP) is a novel regional technique for anesthesia or analgesia. Originally the ESP block was described in 2016 in a case report regarding analgesia intervention for a case of thoracic neuropathic pain. Since then, there has been growing interest and research adding experience about the ESP block as regional anesthetic and analgesic technique. Reviewing the literature about this novel technique in databases like PubMed using the key words "erector spinae plane block" returns approximately 56 publications. So far there is no available big series of cases or reviews regarding the ESP block. The literature is limited to case reports or case series. With the present case we are interested in exploring the efficacy of ESP block as a postoperative analgesic method for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. We describe the case of a 76-year-old female patient scheduled for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Written informed consent was granted (for procedure and publication of photos). We applied a bilateral ultrasound-guided ESP block at T6 level while the patient was awake before general anesthesia induction. The anesthetic solution we used consisted of 12 mL Ropivacaine 0.375% plus 2 mg dexamethasone (on each side). After the successful administration of the block (observation of the solution spread between transverse process and the erector spinae muscles), general anesthesia was induced and the procedure was started. Procedure and recovery was uneventful with the patient experiencing very good analgesia (NRS pain score 0 up to 6 hours after block placement). The patient presented mild pain (NRS score of 2-3) after 6 hours and requested the "on demand" pain medication (1 g paracetamol IV) only 10 hours after the ESP block (NRS pain score of 4-5). The patient experienced no nausea or vomiting, was mobilized easily about 6 hours after the block and was discharged the next day. This relatively simple and safe block dramatically reduced the amount of IV pain medication we usually administer for the specific procedure. The overall result was increased satisfaction of the patient and avoidance of opioid use.
Keywords: plane block; postoperative analgesia; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Bisgaard T. Analgesic treatment after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a critical assessment of the evidence. Anesthesiology. 2006;104(4):835–846. - PubMed
-
- Benyamin R, Trescot AM, Etal DS. Opioid complications and side effects. Pain Physician. 2008;11(2 Suppl):105–120. - PubMed
-
- Forero M, Adhikary SD, Lopez H, Tsui C, Chin KJ. The erector spinae plane block: a novel analgesic technique in thoracic neuropathic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016;41(5):621–627. - PubMed
-
- Ueshima H, Hiroshi O. Spread of local anesthetic solution in the erector spinae plane block. J Clin Anesth. 2018;45:23. - PubMed
-
- El-Boghdadly K, Pawa A. The erector spinae plane block: plane and simple. Anaesthesia. 2017;72(4):434–438. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical