Role of PET/CT in the Evaluation of Aortic Disease
- PMID: 30288369
- PMCID: PMC6165921
- DOI: 10.4068/cmj.2018.54.3.143
Role of PET/CT in the Evaluation of Aortic Disease
Abstract
Positron emission tomography (PET) /computed tomography (CT) has been established as a standard imaging modality in the evaluation of malignancy. Although PET/CT has played a major role in the management of oncology patients, its clinical use has also increased for various disorders other than malignancy. Growing evidence shows that PET/CT images have many advantages in aortic disease as well. This review article addresses the potential role of PET/CT in diseases involving the aorta, emphasizing its usefulness with regard to acute thoracic aortic syndromes, aortic aneurysm, atherosclerotic lesions, aortitis and aortic tumors.
Keywords: Aneurysm; Aortitis; Atherosclerosis; Dissecting; Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT: None declared.
Figures
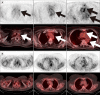
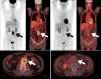
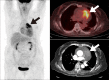
Similar articles
-
[Clinical, laboratory, radiological features, and outcome in 26 patients with aortic involvement amongst a case series of 63 patients with giant cell arteritis].Rev Med Interne. 2014 Jan;35(1):4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Rev Med Interne. 2014. PMID: 23906779 French.
-
IgG4-aortitis among thoracic aortic aneurysms.Heart. 2019 Oct;105(20):1583-1589. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-314499. Epub 2019 May 21. Heart. 2019. PMID: 31113807
-
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography improves diagnostics of inflammatory arteritis.Heart Vessels. 2005 Jul;20(4):179-83. doi: 10.1007/s00380-004-0808-2. Heart Vessels. 2005. PMID: 16025370
-
Aortic involvement in giant cell arteritis: current data.Joint Bone Spine. 2011 May;78(3):246-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Joint Bone Spine. 2011. PMID: 21030278 Review.
-
PET/CT and vascular disease: current concepts.Eur J Radiol. 2011 Oct;80(1):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.12.102. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Eur J Radiol. 2011. PMID: 21371842 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal Aortic Wall Properties in Women with Turner Syndrome.Aorta (Stamford). 2020 Oct;8(5):121-131. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1714384. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Aorta (Stamford). 2020. PMID: 33368097 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic Sources of Embolism.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 15;11:606663. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.606663. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33519684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syphilitic Aortitis with Concomitant Neurosyphilis in Asymptomatic Patient.Emerg Infect Dis. 2025 Jul;31(7):1486-1489. doi: 10.3201/eid3107.250646. Emerg Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40562738 Free PMC article.
-
PET Scan with Fludeoxyglucose/Computed Tomography in Low-Grade Vascular Inflammation.PET Clin. 2020 Apr;15(2):207-213. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2019.11.009. PET Clin. 2020. PMID: 32145891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal Cardiac Imaging in the Assessment of Patients Who Have Suffered a Cardioembolic Stroke: A Review.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Dec 31;11(1):13. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11010013. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 38248883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klompas M. Does this patient have an acute thoracic aortic dissection? JAMA. 2002;287:2262–2272. - PubMed
-
- Mirvis SE, Bidwell JK, Buddemeyer EU, Diaconis JN, Pais SO, Whitley JE, et al. Value of chest radiography in excluding traumatic aortic rupture. Radiology. 1987;163:487–493. - PubMed
-
- Schwab CW, Lawson RB, Lind JF, Garland LW. Aortic injury: comparison of supine and upright portable chest films to evaluate the widened mediastinum. Ann Emerg Med. 1984;13:896–899. - PubMed
-
- Salvolini L, Renda P, Fiore D, Scaglione M, Piccoli G, Giovagnoni A. Acute aortic syndromes: role of multi-detector row CT. Eur J Radiol. 2008;65:350–358. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

