Mutation Profiles in Glioblastoma 3D Oncospheres Modulate Drug Efficacy
- PMID: 30289729
- PMCID: PMC7058093
- DOI: 10.1177/2472630318803749
Mutation Profiles in Glioblastoma 3D Oncospheres Modulate Drug Efficacy
Abstract
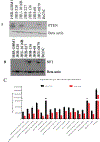
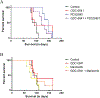
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a lethal brain cancer with a median survival time of approximately 15 months following treatment. Common in vitro GBM models for drug screening are adherent and do not recapitulate the features of human GBM in vivo. Here we report the genomic characterization of nine patient-derived, spheroid GBM cell lines that recapitulate human GBM characteristics in orthotopic xenograft models. Genomic sequencing revealed that the spheroid lines contain alterations in GBM driver genes such as PTEN, CDKN2A, and NF1. Two spheroid cell lines, JHH-136 and JHH-520, were utilized in a high-throughput drug screen for cell viability using a 1912-member compound library. Drug mechanisms that were cytotoxic in both cell lines were Hsp90 and proteasome inhibitors. JHH-136 was uniquely sensitive to topoisomerase 1 inhibitors, while JHH-520 was uniquely sensitive to Mek inhibitors. Drug combination screening revealed that PI3 kinase inhibitors combined with Mek or proteasome inhibitors were synergistic. However, animal studies to test these drug combinations in vivo revealed that Mek inhibition alone was superior to the combination treatments. These data show that these GBM spheroid lines are amenable to high-throughput drug screening and that this dataset may deliver promising therapeutic leads for future GBM preclinical studies.
Keywords: drug combination screening; glioblastoma; high-throughput screening; spheroid.
Figures


References
-
- Nabors LB; Portnow J; Ammirati M; et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 1.2015. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2015, 13, 1191–202. - PubMed
-
- Gallia GL; Brem S; Brem H. Local treatment of malignant brain tumors using implantable chemotherapeutic polymers. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2005, 3, 721–8. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R; Mason WP; van den Bent MJ; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 987–96. - PubMed
-
- Walker MD; Green SB; Byar DP; et al. Randomized comparisons of radiotherapy and nitrosoureas for the treatment of malignant glioma after surgery. N Engl J Med 1980, 303, 1323–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
