Effects of climatically-modulated changes in solar radiation and wind speed on spring phytoplankton community dynamics in Lake Taihu, China
- PMID: 30289946
- PMCID: PMC6173452
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205260
Effects of climatically-modulated changes in solar radiation and wind speed on spring phytoplankton community dynamics in Lake Taihu, China
Abstract
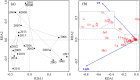
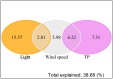
Many studies have focused on the interactive effects of temperature increases due to global warming and nutrient enrichment on phytoplankton communities. Recently, non-temperature effects of climate change (e.g., decreases in wind speed and increases in solar radiation) on large lakes have received increasing attention. To evaluate the relative contributions of both temperature and non-temperature effects on phytoplankton communities in a large eutrophic subtropical shallow lake, we analyzed long-term monitoring data from Lake Taihu, China from 1997 to 2016. Results showed that Lake Taihu's spring phytoplankton biovolume and composition changed dramatically over this time frame, with a change in dominant species. Stepwise multiple linear regression models indicated that spring phytoplankton biovolume was strongly influenced by total phosphorus (TP), light condition, wind speed and total nitrogen (TN) (radj2 = 0.8, p < 0.01). Partial redundancy analysis (pRDA) showed that light condition accounted for the greatest variation of phytoplankton community composition, followed by TP and wind speed, as well as the interactions between TP and wind speed. Our study points to the additional importance of non-temperature effects of climate change on phytoplankton community dynamics in Lake Taihu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Bopp L, Resplandy L, Orr JC, Doney SC, Dunne JP, Gehlen M, et al. Multiple stressors of ocean ecosystems in the 21st century: projections with CMIP5 models. Biogeosciences. 2013; 10:6225–45.
-
- Elliott JA. The seasonal sensitivity of cyanobacteria and other phytoplankton to changes in flushing rate and water temperature. Glob Change Biol. 2010; 16(2):864–76.
-
- Sommer U, Lengfellner K. Climate change and the timing, magnitude, and composition of the phytoplankton spring bloom. Glob Change Biol. 2008; 14(6):1199–208.
-
- O’Neil J, Davis T, Burford M, Gobler C. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae. 2012; 14:313–34.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

