99mTc-MIBI single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for the incidental detection of rare parathyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 30290620
- PMCID: PMC6200521
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012578
99mTc-MIBI single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for the incidental detection of rare parathyroid carcinoma
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the characteristics of parathyroid carcinoma and to validate the diagnostic value of Tc-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) single photon emission computed tomography/x-ray computed tomography (SPECT/CT) for differentiating between parathyroid carcinoma and hyperparathyroidism. Four consecutive patients with suspected primary hyperparathyroidism were enrolled in this study and underwent Tc-MIBI SPECT/CT, ultrasonography, enhanced CT, and MRI. Serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcium were measured. All primary and recurrent lesions showed high focal uptake on Tc-MIBI image, whereas metastatic lymph nodes gave false negative results. The serum PTH was 165.14 ± 90.26 pmol/L, which declined rapidly after surgery. One patient with a persistently high PTH (147.5 pmol/L) after surgery presented with multiple lymphadenopathy in the neck. Higher expression of chromogranin A (CgA) further confirmed parathyroid carcinoma as a rare endocrine tumor. Parathyroid carcinoma is thus usually diagnosed incidentally based on nonspecific multiorgan symptoms of hypercalcemia and hyperparathyroidism. Tc-MIBI SPECT/CT may help to localize the parathyroid carcinoma, while MRI is valuable for detecting metastasis. Serum PTH and CgA serve as circulating biomarkers in parathyroid carcinoma, and raised levels of PTH and CgA together with locoregional lymphadenopathy may indicate parathyroid carcinoma. Further studies are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

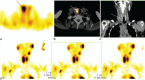
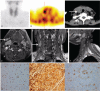
References
-
- Wei CH, Harari A. Parathyroid carcinoma: update and guidelines for management. Curr Treat Opt Oncol 2012;13:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Medas F, Erdas E, Loi G, et al. Controversies in the management of parathyroid carcinoma: a case series and review of the literature. Int J Surg 2016;28:S94–8. - PubMed
-
- Lee YS, Hong SW, Jeong JJ, et al. Parathyroid carcinoma: a 16-year experience in a single institution. Endocr J 2010;57:493–7. - PubMed
-
- Kassahun WT, Jonas S. Focus on parathyroid carcinoma. Int J Surg 2011;9:13–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee PK, Jarosek SL, Virnig BA, et al. Trends in the incidence and treatment of parathyroid cancer in the United States. Cancer 2007;109:1736–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

