pH-dependent regulation of SQSTM1/p62 during autophagy
- PMID: 30290711
- PMCID: PMC6287675
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1532264
pH-dependent regulation of SQSTM1/p62 during autophagy
Abstract
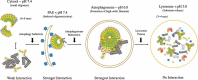
During macroautophagy/autophagy, SQSTM1/p62 plays dual roles as a key mediator of cargo selection and as an autophagic substrate. SQSTM1 links N-degrons and/or ubiquitinated cargoes to the autophagosome by forming homo- or hetero-oligomers, although its N-degron recognition and oligomerization mechanisms are not well characterized. We recently found that SQSTM1 is a novel type of N-recognin whose ZZ domain provides a negatively-charged binding pocket for Arg-charged N-degron (Nt-Arg), a prototype type-1 substrate. Although differences in binding affinity exist for each N-degron, SQSTM1 also interacts with type-2 N-degrons, such as Nt-Tyr and Nt-Trp. Intriguingly, interactions between SQSTM1's ZZ domain and various N-degrons are greatly influenced by pH-dependent SQSTM1 oligomerization via its PB1 domain. Because cellular pH conditions vary from neutral to acidic depending on the stage of autophagy, the pH-dependent regulation of SQSTM1's oligomerization must be tightly coupled with the autophagic process.
Keywords: Aggrephagy; HSPA5/BiP/GRP78; N-end rule; UBR box; autophagy adaptor; pH-dependent oligomerization.
Figures
Comment on
-
Insights into degradation mechanism of N-end rule substrates by p62/SQSTM1 autophagy adapter.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 17;9(1):3291. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05825-x. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30120248 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
