Evidence of Local Concentration of α-Particles from 211At-Labeled Antibodies in Liver Metastasis Tissue
- PMID: 30291193
- PMCID: PMC6448461
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.118.216853
Evidence of Local Concentration of α-Particles from 211At-Labeled Antibodies in Liver Metastasis Tissue
Abstract
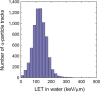
We investigated the local concentration of α-particles from 211At-labeled trastuzumab antibodies against human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 antigens in liver metastasis tissue of mice. Methods: Mice carrying metastatic cancer in their liver were injected with 211At-agent. After 12 h, the liver was removed and sliced, and 2 tissue samples of liver tissues without lesions and one containing metastatic lesions were mounted on the CR-39 plastic nuclear track detector. Microscope images of the tissues on the CR-39 were acquired. After irradiation for 31 h, the tissues were removed from the CR-39. A microscope image of α-particle tracks on the CR-39 was acquired after chemical etching. The positions of each tissue sample and the emitted α-particle tracks were adjusted to the same coordinates. Results: The positional distribution of α-particle tracks emitted from 211At was consistent within the tissue. The α-particle tracks were mainly allocated in the tumor region of the tissue. The absorbed dose in individual cells segmented by 10-μm intervals was obtained by the spectroscopic analysis of the linear-energy-transfer spectrum. The concentration efficiency-the track density ratio of α-particle tracks in the necrotized tissue, which was the tumor region, to the normal tissue-was found to be 6.0 ± 0.2. In the tumor region, the high-linear-energy-transfer α-particles deposited a large enough dose to cause lethal damage to the cancer cells. Conclusion: The total absorbed dose ranged from 1 to 7 Gy with a peak at around 2 Gy, which would correspond to a 2-3 times higher biologically equivalent dose because of the high relative biological effectiveness of the α-particles emitted from 211At.
Keywords: 211At radionuclide; autoradiography; dose distribution; microscopy; radioimmunotherapy; α-particle.
© 2019 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures



References
-
- Newman HC, Prise KM, Folkard M, Michael BD. DNA double-strand break distributions in x-ray and alpha-particle irradiated V79 cells: evidence for non-random breakage. Int J Radiat Biol. 1997;71:347–363. - PubMed
-
- Bruland ØS, Nilsson S, Fisher DR, Larsen RH. High-linear energy transfer irradiation targeted to skeletal metastases by the alpha emitter 223Ra: adjuvant or alternative to conventional modalities? Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6250s–6257s. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson S, Franzén L, Parker C, et al. Bone-targeted radium-223 in symptomatic, hormone-refractory prostate cancer: a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase II study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:587–594. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson S, Larsen RH, Fosså SD, et al. First clinical experience with alpha-emitting radium-223 in the treatment of skeletal metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:4451–4459. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson S, Strang P, Aksnes AK, et al. A randomized, dose–response, multicenter phase II study of radium-223 chloride for the palliation of painful bone metastases in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:678–686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
