Efficacy and Safety of High-Specific-Activity 131I-MIBG Therapy in Patients with Advanced Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma
- PMID: 30291194
- PMCID: PMC6495236
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.118.217463
Efficacy and Safety of High-Specific-Activity 131I-MIBG Therapy in Patients with Advanced Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma
Abstract
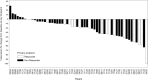
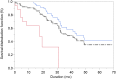
Patients with metastatic or unresectable (advanced) pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL) have poor prognoses and few treatment options. This multicenter, phase 2 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of high-specific-activity 131I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine (HSA 131I-MIBG) in patients with advanced PPGL. Methods: In this open-label, single-arm study, 81 PPGL patients were screened for enrollment, and 74 received a treatment-planning dose of HSA 131I-MIBG. Of these patients, 68 received at least 1 therapeutic dose (∼18.5 GBq) of HSA 131I-MIBG intravenously. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in baseline antihypertensive medication use lasting at least 6 mo. Secondary endpoints included objective tumor response as assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.0, biochemical tumor marker response, overall survival, and safety. Results: Of the 68 patients who received at least 1 therapeutic dose of HSA 131I-MIBG, 17 (25%; 95% confidence interval, 16%-37%) had a durable reduction in baseline antihypertensive medication use. Among 64 patients with evaluable disease, 59 (92%) had a partial response or stable disease as the best objective response within 12 mo. Decreases in elevated (≥1.5 times the upper limit of normal at baseline) serum chromogranin levels were observed, with confirmed complete and partial responses 12 mo after treatment in 19 of 28 patients (68%). The median overall survival was 36.7 mo (95% confidence interval, 29.9-49.1 mo). The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were nausea, myelosuppression, and fatigue. No patients had drug-related acute hypertensive events during or after the administration of HSA 131I-MIBG. Conclusion: HSA 131I-MIBG offers multiple benefits, including sustained blood pressure control and tumor response in PPGL patients.
Keywords: high-specific-activity 131I-MIBG; neuroendocrine tumors; paraganglioma; pheochromocytoma; rare; ultra-orphan disease.
© 2019 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Davison AS, Jones DM, Ruthven S, Helliwell T, Shore SL. Clinical evaluation and treatment of phaeochromocytoma. Ann Clin Biochem. 2018;55:34–48. - PubMed
-
- Lenders JW, Eisenhofer G, Mannelli M, Pacak K. Phaechromocytoma. Lancet. 2005;366:665–675. - PubMed
-
- Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Treatment (PDQ®)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute website. https://www.cancer.gov/types/pheochromocytoma/hp/pheochromocytoma-treatm...; last updated February 18, 2018. Accessed December 20, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
