IL-17A-associated IKK-α signaling induced TSLP production in epithelial cells of COPD patients
- PMID: 30291224
- PMCID: PMC6173689
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-018-0158-2
IL-17A-associated IKK-α signaling induced TSLP production in epithelial cells of COPD patients
Abstract
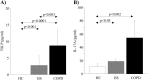
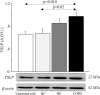
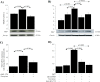
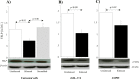
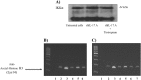
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a cytokine expressed in the epithelium, involved in the pathogenesis of chronic disease. IL-17A regulates airway inflammation, oxidative stress, and reduction of steroid sensitivity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). TSLP and IL-17A were measured in induced sputum supernatants (ISs) from healthy controls (HC), healthy smokers (HS), and COPD patients by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Human bronchial epithelial cell line (16HBE) and normal bronchial epithelial cells were stimulated with rhIL-17A or ISs from COPD patients to evaluate TSLP protein and mRNA expression. The effects of the depletion of IL-17A in ISs, an anticholinergic drug, and the silencing of inhibitor kappa kinase alpha (IKKα) on TSLP production were evaluated in 16HBE cells. Coimmunoprecipitation of acetyl-histone H3(Lys14)/IKKα was evaluated in 16HBE cells treated with rhIL-17A and in the presence of the drug. TSLP and IL-17A levels were higher in ISs from COPD patients and HS compared with HC. TSLP protein and mRNA increased in 16HBE cells and in normal bronchial epithelial cells stimulated with ISs from COPD patients compared with ISs from HC and untreated cells. IKKα silencing reduced TSLP production in 16HBE cells stimulated with rhIL-17A and ISs from COPD patients. RhIL-17A increased the IKKα/acetyl-histone H3 immunoprecipitation in 16HBE cells. The anticholinergic drug affects TSLP protein and mRNA levels in bronchial epithelial cells treated with rhIL-17A or with ISs from COPD patients, and IKKα mediated acetyl-histone H3(Lys14). IL-17A/IKKα signaling induced the mechanism of chromatin remodeling associated with acetyl-histone H3(Lys14) and TSLP production in bronchial epithelial cells. Anticholinergic drugs might target TSLP derived from epithelial cells during the treatment of COPD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting interleukin-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin pathways for novel pulmonary therapeutics in asthma and COPD.Eur Respir Rev. 2023 Jan 25;32(167):220144. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0144-2022. Print 2023 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. PMID: 36697211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expressions of TSLP, IL-33, and IL-17A in Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells from Asthma and COPD Patients are Related to Epithelial-Macrophage Interactions.Cells. 2020 Aug 22;9(9):1944. doi: 10.3390/cells9091944. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32842623 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A induces chromatin remodeling promoting IL-8 release in bronchial epithelial cells: Effect of Tiotropium.Life Sci. 2016 May 1;152:107-16. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.03.031. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27038884
-
Increased TSLP and oxidative stress reflect airway epithelium injury upon cigarette smoke exposure. Is there a role for carbocysteine?Toxicology. 2025 Aug;515:154160. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2025.154160. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Toxicology. 2025. PMID: 40280536
-
Function and mechanisms of TSLP/TSLPR complex in asthma and COPD.Clin Exp Allergy. 2012 Jul;42(7):994-1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03919.x. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012. PMID: 22168549 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular and Molecular Signatures of Oxidative Stress in Bronchial Epithelial Cell Models Injured by Cigarette Smoke Extract.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1770. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031770. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting interleukin-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin pathways for novel pulmonary therapeutics in asthma and COPD.Eur Respir Rev. 2023 Jan 25;32(167):220144. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0144-2022. Print 2023 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. PMID: 36697211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expressions of TSLP, IL-33, and IL-17A in Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells from Asthma and COPD Patients are Related to Epithelial-Macrophage Interactions.Cells. 2020 Aug 22;9(9):1944. doi: 10.3390/cells9091944. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32842623 Free PMC article.
-
Determining Pharmacological Mechanisms of Chinese Incompatible Herbs Fuzi and Banxia in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systems Pharmacology-Based Study.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Dec 31;2020:8365603. doi: 10.1155/2020/8365603. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33488748 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Biological Functions of IL-17A: A New Target in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 2;12:695957. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.695957. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34305606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

