Oleoylethanolamide treatment affects gut microbiota composition and the expression of intestinal cytokines in Peyer's patches of mice
- PMID: 30291258
- PMCID: PMC6173739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32925-x
Oleoylethanolamide treatment affects gut microbiota composition and the expression of intestinal cytokines in Peyer's patches of mice
Abstract
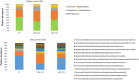
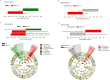
The lipid sensor oleoylethanolamide (OEA), an endogenous high-affinity agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) secreted in the proximal intestine, is endowed with several distinctive homeostatic properties, such as control of appetite, anti-inflammatory activity, stimulation of lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation. When administered exogenously, OEA has beneficial effects in several cognitive paradigms; therefore, in all respects, OEA can be considered a hormone of the gut-brain axis. Here we report an unexplored modulatory effect of OEA on the intestinal microbiota and on immune response. Our study shows for the first time that sub-chronic OEA administration to mice fed a normal chow pellet diet, changes the faecal microbiota profile, shifting the Firmicutes:Bacteroidetes ratio in favour of Bacteroidetes (in particular Bacteroides genus) and decreasing Firmicutes (Lactobacillus), and reduces intestinal cytokines expression by immune cells isolated from Peyer's patches. Our results suggest that sub-chronic OEA treatment modulates gut microbiota composition towards a "lean-like phenotype", and polarises gut-specific immune responses mimicking the effect of a diet low in fat and high in polysaccharides content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
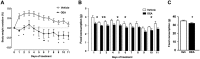



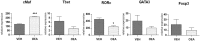
Similar articles
-
Fucoidan modulates gut microbiota and immunity in Peyer's patches against inflammatory bowel disease.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Oct 15;342:122421. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122421. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 39048206
-
Oleoylethanolamide-producing Lactobacillus paracasei F19 improves metabolic and behavioral disorders by restoring intestinal permeability and microbiota-gut-brain axis in high-fat diet-induced obese male mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2025 Jul;127:25-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2025.02.014. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2025. PMID: 39988008
-
Oleoylethanolamide, an endogenous PPAR-alpha agonist, lowers body weight and hyperlipidemia in obese rats.Neuropharmacology. 2005 Jun;48(8):1147-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.02.013. Epub 2005 Apr 21. Neuropharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15910890
-
Oleoylethanolamide: The role of a bioactive lipid amide in modulating eating behaviour.Obes Rev. 2018 Feb;19(2):178-197. doi: 10.1111/obr.12630. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Obes Rev. 2018. PMID: 29124885 Review.
-
A systematic review of the effects of oleoylethanolamide, a high-affinity endogenous ligand of PPAR-α, on the management and prevention of obesity.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020 Apr;47(4):543-552. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13238. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31868943
Cited by
-
Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals the Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Resistance to Salmonella Enteritidis Colonization in Chicken.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 2;24(5):4824. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054824. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902251 Free PMC article.
-
Probing and manipulating the gut microbiome with chemistry and chemical tools.Gut Microbiome (Camb). 2025 Apr 14;6:e6. doi: 10.1017/gmb.2025.4. eCollection 2025. Gut Microbiome (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40336799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota and oleoylethanolamide in the regulation of intestinal homeostasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 5;14:1135157. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1135157. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37091842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological potential of endocannabinoid and endocannabinoid-like compounds in protecting intestinal structure and metabolism under high-fat conditions.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 22;16:1567543. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1567543. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40474970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high docosahexaenoic acid diet alters lung inflammation and recovery following repetitive exposure to aqueous organic dust extracts.J Nutr Biochem. 2021 Nov;97:108797. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108797. Epub 2021 Jun 12. J Nutr Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34126202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sáez de Guinoa Julia, Jimeno Rebeca, Gaya Mauro, Kipling David, Garzón María José, Dunn‐Walters Deborah, Ubeda Carles, Barral Patricia. CD1d‐mediated lipid presentation by CD11c + cells regulates intestinal homeostasis . The EMBO Journal. 2018;37(5):e97537. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797537. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

