Novel multiplex PCR-SSP method for centromeric KIR allele discrimination
- PMID: 30291273
- PMCID: PMC6173694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33135-1
Novel multiplex PCR-SSP method for centromeric KIR allele discrimination
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Novel multiplex PCR-SSP method for centromeric KIR allele discrimination.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 18;9(1):15210. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43449-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31628342 Free PMC article.
Abstract
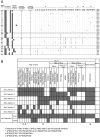
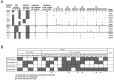
Allelic diversity of the KIR2DL receptors drive differential expression and ligand-binding affinities that impact natural killer cell function and patient outcomes for diverse cancers. We have developed a global intermediate resolution amplification-refractory mutation system (ARMS) PCR-SSP method for distinguishing functionally relevant subgroups of the KIR2DL receptors, as defined by phylogenetic study of the protein sequences. Use of the ARMS design makes the method reliable and usable as a kit, with all reactions utilizing the same conditions. Six reactions define six subgroups of KIR2DL1; four reactions define three subgroups of KIR2DL2; and five reactions define four subgroups of KIR2DL3. Using KIR allele data from a cohort of 426 European-Americans, we identified the most common KIR2DL subtypes and developed the high-throughput PCR-based methodology, which was validated on a separate cohort of 260 healthy donors. Linkage disequilibrium analysis between the different KIR2DL alleles revealed that seven allelic combinations represent more than 95% of the observed population genotypes for KIR2DL1/L2/L3. In summary, our findings enable rapid typing of the most common KIR2DL receptor subtypes, allowing more accurate prediction of co-inheritance and providing a useful tool for the discrimination of observed differences in surface expression and effector function among NK cells exhibiting disparate KIR2DL allotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have the following interests: The method of KIR2DL alleles typing described in this manuscript was submitted by Drs Jean-Benoît LE LUDUEC and Katharine C. Hsu (Methods and Kits for typing KIR2DL alleles, U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. PCT/US2017/054172). The authors confirm that this does not alter their adherence to Scientific Reports policies on materials and data sharing.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

