Amygdala subnuclei and healthy cognitive aging
- PMID: 30291764
- PMCID: PMC6865708
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24353
Amygdala subnuclei and healthy cognitive aging
Abstract
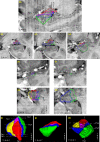
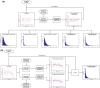
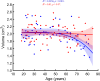
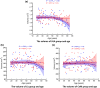
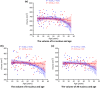
Amygdala is a group of nuclei involved in the neural circuits of fear, reward learning, and stress. The main goal of this magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study was to investigate the relationship between age and the amygdala subnuclei volumes in a large cohort of healthy individuals. Our second goal was to determine effects of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) polymorphisms on the amygdala structure. One hundred and twenty-six healthy participants (18-85 years old) were recruited for this study. MRI datasets were acquired on a 4.7 T system. Amygdala was manually segmented into five major subdivisions (lateral, basal, accessory basal nuclei, and cortical, and centromedial groups). The BDNF (methionine and homozygous valine) and APOE genotypes (ε2, homozygous ε3, and ε4) were obtained using single nucleotide polymorphisms. We found significant nonlinear negative associations between age and the total amygdala and its lateral, basal, and accessory basal nuclei volumes, while the cortical amygdala showed a trend. These age-related associations were found only in males but not in females. Centromedial amygdala did not show any relationship with age. We did not observe any statistically significant effects of APOE and BDNF polymorphisms on the amygdala subnuclei volumes. In contrast to APOE ε2 allele carriers, both older APOE ε4 and ε3 allele carriers had smaller lateral, basal, accessory basal nuclei volumes compared to their younger counterparts. This study indicates that amygdala subnuclei might be nonuniformly affected by aging and that age-related association might be gender specific.
Keywords: aging; amygdala subnuclei; apolipoprotein E (APOE); brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Abe, O. , Yamasue, H. , Yamada, H. , Masutani, Y. , Kabasawa, H. , Sasaki, H. , … Ohtomo, K. (2010). Sex dimorphism in gray/white matter volume and diffusion tensor during normal aging. NMR in Biomedicine, 23, 446–458. - PubMed
-
- Allen, J. S. , Bruss, J. , Brown, C. K. , & Damasio, H. (2005). Normal neuroanatomical variation due to age: The major lobes and a parcellation of the temporal region. Neurobiology of Aging, 26, 1245–1260 discussion 1279‐1282. - PubMed
-
- Basso, M. , Gelernter, J. , Yang, J. , MacAvoy, M. G. , Varma, P. , Bronen, R. A. , & van Dyck, C. H. (2006). Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 is associated with atrophy of the amygdala in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 2710, 1416–1424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

