Surfactant Proteins A and D: Trimerized Innate Immunity Proteins with an Affinity for Viral Fusion Proteins
- PMID: 30293076
- PMCID: PMC6738215
- DOI: 10.1159/000492974
Surfactant Proteins A and D: Trimerized Innate Immunity Proteins with an Affinity for Viral Fusion Proteins
Abstract
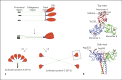
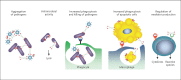
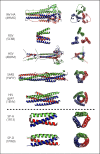
Innate recognition of viruses is an essential part of the immune response to viral pathogens. This is integral to the maintenance of healthy lungs, which are free from infection and efficient at gaseous exchange. An important component of innate immunity for identifying viruses is the family of C-type collagen-containing lectins, also known as collectins. These secreted, soluble proteins are pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) which recognise pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), including viral glycoproteins. These innate immune proteins are composed of trimerized units which oligomerise into higher-order structures and facilitate the clearance of viral pathogens through multiple mechanisms. Similarly, many viral surface proteins form trimeric configurations, despite not showing primary protein sequence similarities across the virus classes and families to which they belong. In this review, we discuss the role of the lung collectins, i.e., surfactant proteins A and D (SP-A and SP-D) in viral recognition. We focus particularly on the structural similarity and complementarity of these trimeric collectins with the trimeric viral fusion proteins with which, we hypothesise, they have elegantly co-evolved. Recombinant versions of these innate immune proteins may have therapeutic potential in a range of infectious and inflammatory lung diseases including anti-viral therapeutics.
Keywords: Collectins; Fusion proteins; Innate immunity; Structure; Surfactant proteins; Trimeric proteins; Virus.
© 2018 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Koeppen BM, Stanton BA. Berne & Levy physiology - updated edition. 6th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Mosby/Elsevier; 2009.
-
- Persson A, Rust K, Chang D, Moxley M, Longmore W, Crouch E. CP4: a pneumocyte-derived collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Evidence for heterogeneity of collagenous surfactant proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov;27((23)):8576–84. - PubMed
-
- Hawgood S, Benson BJ, Hamilton RL. Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan;24((1)):184–90. - PubMed
-
- Possmayer F. A proposed nomenclature for pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138((4)):990–8. - PubMed
-
- Persson A, Chang D, Rust K, Moxley M, Longmore W, Crouch E. Purification and biochemical characterization of CP4 (SP-D), a collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul;28((15)):6361–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

