Velocity Curvature Index: a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker for Large Vessel Occlusion
- PMID: 30293170
- PMCID: PMC6733810
- DOI: 10.1007/s12975-018-0667-2
Velocity Curvature Index: a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker for Large Vessel Occlusion
Abstract
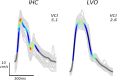
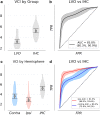
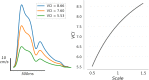
Despite being a conveniently portable technology for stroke assessment, Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD) remains widely underutilized due to complex training requirements necessary to reliably obtain and interpret cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) waveforms. The validation of objective TCD metrics for large vessel occlusion (LVO) represents a first critical step toward enabling use by less formally trained personnel. In this work, we assess the diagnostic utility, relative to current standard CT angiography (CTA), of a novel TCD-derived biomarker for detecting LVO. Patients admitted to the hospital with stroke symptoms underwent TCD screening and were grouped into LVO and control groups based on the presence of CTA confirmed occlusion. Velocity curvature index (VCI) was computed from CBFV waveforms recorded at multiple depths from the middle cerebral arteries (MCA) of both cerebral hemispheres. VCI was assessed for 66 patients, 33 of which had occlusions of the MCA or internal carotid artery. Our results show that VCI was more informative when measured from the cerebral hemisphere ipsilateral to the site of occlusion relative to contralateral. Moreover, given any pair of bilateral recordings, VCI separated LVO patients from controls with average area under receiver operating characteristic curve of 92%, which improved to greater than 94% when pairs were selected by maximal velocity. We conclude that VCI is an analytically valid candidate biomarker for LVO diagnosis, possessing comparable accuracy, and several important advantages, relative to current TCD diagnostic methodologies.
Keywords: Diagnostic imaging; Ischemic stroke; Large vessel occlusion; Transcranial Doppler; Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Samuel G. Thorpe, Corey M. Thibeault, Seth J. Wilk, Michael O’Brien, Nicolas Canac, Mina Ranjbaran, and Robert B. Hamilton are employed by and hold stock options in Neural Analytics, Inc. Thomas Devlin is a paid consultant and stockholder of Neural Analytics, Inc. Christian Devlin declares that he has no conflicts to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Saqqur M, Uchino K, Demchuk AM, Molina CA, Garami Z, Calleja S, Akhtar N, Orouk FO, Salam A, Shuaib A, Alexandrov AV, for CLOTBUST Investigators Site of arterial occlusion identified by transcranial Doppler predicts the response to intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Stroke. 2007;38(3):948–954. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000257304.21967.ba. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, van der Lugt A, Menon BK, Majoie CBLM, Dippel DW, Campbell BC, Nogueira RG, Demchuk AM, Tomasello A, Cardona P, Devlin TG, Frei DF, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Berkhemer OA, Jovin TG, Siddiqui AH, van Zwam WH, Davis SM, Castaño C, Sapkota BL, Fransen PS, Molina C, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Chamorro Á, Lingsma H, Silver FL, Donnan GA, Shuaib A, Brown S, Stouch B, Mitchell PJ, Davalos A, Roos YBWEM, Hill MD, for the HERMES Collaborators Time to treatment with endovascular thrombectomy and outcomes from ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016;316(12):1279–1288. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.13647. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

