Preserving Insulin Secretion in Diabetes by Inhibiting VDAC1 Overexpression and Surface Translocation in β Cells
- PMID: 30293774
- PMCID: PMC6331340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.008
Preserving Insulin Secretion in Diabetes by Inhibiting VDAC1 Overexpression and Surface Translocation in β Cells
Abstract
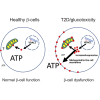
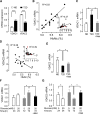
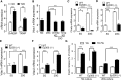
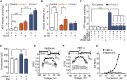
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) develops after years of prediabetes during which high glucose (glucotoxicity) impairs insulin secretion. We report that the ATP-conducting mitochondrial outer membrane voltage-dependent anion channel-1 (VDAC1) is upregulated in islets from T2D and non-diabetic organ donors under glucotoxic conditions. This is caused by a glucotoxicity-induced transcriptional program, triggered during years of prediabetes with suboptimal blood glucose control. Metformin counteracts VDAC1 induction. VDAC1 overexpression causes its mistargeting to the plasma membrane of the insulin-secreting β cells with loss of the crucial metabolic coupling factor ATP. VDAC1 antibodies and inhibitors prevent ATP loss. Through direct inhibition of VDAC1 conductance, metformin, like specific VDAC1 inhibitors and antibodies, restores the impaired generation of ATP and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in T2D islets. Treatment of db/db mice with VDAC1 inhibitor prevents hyperglycemia, and maintains normal glucose tolerance and physiological regulation of insulin secretion. Thus, β cell function is preserved by targeting the novel diabetes executer protein VDAC1.
Keywords: ATP; Ep300(−/−)cells; VDAC; db/db mice; human islets; isolated VDAC1 channel conductance; metformin; mitochondrial metabolism; oxygen consumption rate; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
β Cell Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes: Drained of Energy?Cell Metab. 2019 Jan 8;29(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.12.015. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 30625305
-
Novel mechanism of impaired metabolism-secretion coupling in β-cells: Loss of cytosolic adenosine triphosphate by leakage.J Diabetes Investig. 2019 Nov;10(6):1401-1404. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13094. Epub 2019 Jul 2. J Diabetes Investig. 2019. PMID: 31168903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akanda N., Tofighi R., Brask J., Tamm C., Elinder F., Ceccatelli S. Voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) in the plasma membrane play a critical role in apoptosis in differentiated hippocampal neurons but not in neural stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:3225–3234. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed M., Muhammed S.J., Kessler B., Salehi A. Mitochondrial proteome analysis reveals altered expression of voltage dependent anion channels in pancreatic beta-cells exposed to high glucose. Islets. 2010;2:283–292. - PubMed
-
- Anello M., Lupi R., Spampinato D., Piro S., Masini M., Boggi U., Del Prato S., Rabuazzo A.M., Purrello F., Marchetti P. Functional and morphological alterations of mitochondria in pancreatic beta cells from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2005;48:282–289. - PubMed
-
- Aram L., Geula S., Arbel N., Shoshan-Barmatz V. VDAC1 cysteine residues: topology and function in channel activity and apoptosis. Biochem. J. 2010;427:445–454. - PubMed
-
- Aroda V.R., Knowler W.C., Crandall J.P., Perreault L., Edelstein S.L., Jeffries S.L., Molitch M.E., Pi-Sunyer X., Darwin C., Heckman-Stoddard B.M. Metformin for diabetes prevention: insights gained from the diabetes prevention program/diabetes prevention program outcomes study. Diabetologia. 2017;60:1601–1611. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

