Automatic Inference of Sequence from Low-Resolution Crystallographic Data
- PMID: 30293812
- PMCID: PMC6221995
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2018.08.011
Automatic Inference of Sequence from Low-Resolution Crystallographic Data
Abstract
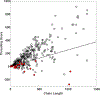
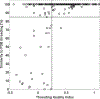
At resolutions worse than 3.5 Å, the electron density is weak or nonexistent at the locations of the side chains. Consequently, the assignment of the protein sequences to their correct positions along the backbone is a difficult problem. In this work, we propose a fully automated computational approach to assign sequence at low resolution. It is based on our surprising observation that standard reciprocal-space indicators, such as the initial unrefined R value, are sensitive enough to detect an erroneous sequence assignment of even a single backbone position. Our approach correctly determines the amino acid type for 15%, 13%, and 9% of the backbone positions in crystallographic datasets with resolutions of 4.0 Å, 4.5 Å, and 5.0 Å, respectively. We implement these findings in an application for threading a sequence onto a backbone structure. For the three resolution ranges, the application threads 83%, 81%, and 64% of the sequences exactly as in the deposited PDB structures.
Keywords: automatic threading; low-resolution crystallography; model building; reciprocal-space indicators.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

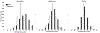


Similar articles
-
Addition of side chains to a known backbone with defined side-chain centroids.Biophys Chem. 2003;100(1-3):261-80. doi: 10.1016/s0301-4622(02)00285-5. Biophys Chem. 2003. PMID: 12646370
-
Prediction of protein-protein interface sequence diversity using flexible backbone computational protein design.Structure. 2008 Dec 10;16(12):1777-88. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2008.09.012. Structure. 2008. PMID: 19081054
-
Crystallographic threading.Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1999:2-9. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10786280
-
New Biological Insights from Better Structure Models.J Mol Biol. 2016 Mar 27;428(6):1375-1393. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26869101 Review.
-
From electron density and sequence to structure: integrating protein image analysis and threading for structure determination.Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1996;4:25-33. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8877501 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence-Similar Protein Domain Pairs With Structural or Topological Dissimilarity.Proteins. 2025 Mar;93(3):588-597. doi: 10.1002/prot.26753. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39392124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen SX, Morris RJ, Fernandez FJ, Ben Jelloul M, Kakaris M, Parthasarathy V, Lamzin VS, Kleywegt GJ, Perrakis A. (2004). Towards complete validated models in the next generation of ARP/wARP. Acta Crystallogr D. 60, 2222–2229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

