Oxytocin Transforms Firing Mode of CA2 Hippocampal Neurons
- PMID: 30293821
- PMCID: PMC6516476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.008
Oxytocin Transforms Firing Mode of CA2 Hippocampal Neurons
Abstract
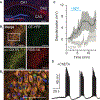
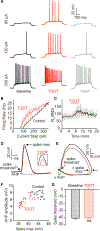
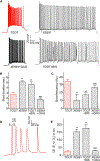
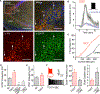
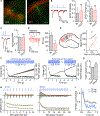
Oxytocin is an important neuromodulator in the mammalian brain that increases information salience and circuit plasticity, but its signaling mechanisms and circuit effect are not fully understood. Here we report robust oxytocinergic modulation of intrinsic properties and circuit operations in hippocampal area CA2, a region of emerging importance for hippocampal function and social behavior. Upon oxytocin receptor activation, CA2 pyramidal cells depolarize and fire bursts of action potentials, a consequence of phospholipase C signaling to modify two separate voltage-dependent ionic processes. A reduction of potassium current carried by KCNQ-based M channels depolarizes the cell; protein kinase C activity attenuates spike rate of rise and overshoot, dampening after-hyperpolarizations. These actions, in concert with activation of fast-spiking interneurons, promote repetitive firing and CA2 bursting; bursting then governs short-term plasticity of CA2 synaptic transmission onto CA1 and, thus, efficacy of information transfer in the hippocampal network.
Keywords: CA2; G-protein coupled receptor; M-current; burst firing; hippocampus; inhibitory interneuron; neuromodulation; oxytocin; pyramidal cell; short term plasticity.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
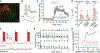
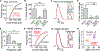
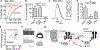
References
-
- Bargmann CI, and Marder E (2013). From the connectome to brain function. Nat. Methods 10, 483–490. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner T, Heinrichs M, Vonlanthen A, Fischbacher U, and Fehr E (2008). Oxytocin shapes the neural circuitry of trust and trust adaptation in humans. Neuron 58, 639–650. - PubMed
-
- Bley KR, and Tsien RW (1990). Inhibition of Ca2+ and K+ channels in sympathetic neurons by neuropeptides and other ganglionic transmitters. Neuron 4, 379–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 NS086750/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH064070/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS021072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007308/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071739/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG025970/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH119136/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025970/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH106744/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F99 NS108552/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH071739/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS024067/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 NS107616/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MH064070/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH106744/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS021072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

