Prognostic Effect of Adenosine-related Genetic Variants in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated With Bevacizumab-based Chemotherapy
- PMID: 30293873
- PMCID: PMC6416082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clcc.2018.09.003
Prognostic Effect of Adenosine-related Genetic Variants in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated With Bevacizumab-based Chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Adenosine has an immunosuppressive and angiogenic modulation of the tumor microenvironment. The present study explored the efficacy of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in adenosine-related molecules for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with bevacizumab-based chemotherapy.
Patients and methods: We analyzed genomic DNA extracted from 451 samples from 3 independent cohorts: a discovery cohort of 107 patients treated with FOLFIRI (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, irinotecan) plus bevacizumab in FIRE-3 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT00433927); a validation cohort of 215 patients with FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in TRIBE (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT00719797); and a control cohort of 129 patients treated with FOLFIRI plus cetuximab in FIRE-3. The relationship between the selected SNPs and clinical outcomes was analyzed.
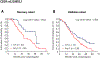
Results: In the discovery cohort, patients with any C allele in CD39 rs11188513 had significantly shorter median progression-free survival compared with those with the T/T variant (11.3 vs. 13.1 months; hazard ratio [HR], 1.70; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04-2.77; P = .022) on univariate analysis. Also, their overall survival (OS) was shorter (27.4 vs. 49.9 months; HR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.07-4.10; P = .031) on univariate and multivariable analyses. The significant association between CD39 rs11188513 and OS was confirmed in the validation cohort (25.8 vs. 31.6 months; HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.09-2.15; P = .013). CD73 rs2229523 and A2BR rs2015353 in the discovery cohort and CD39 rs2226163 in the validation cohort showed significant correlations with OS on univariate and multivariable analyses. None of SNPs were significant in the cetuximab control cohort.
Conclusion: Selected SNPs in the adenosine pathway could affect the clinical outcomes of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab.
Keywords: A2AR; CD39; CD73; SNP; mCRC.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of genetic variations in the MAPK signaling pathway on outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line FOLFIRI and bevacizumab: data from FIRE-3 and TRIBE trials.Ann Oncol. 2017 Nov 1;28(11):2780-2785. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx412. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29045529 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Continuation of Bevacizumab vs Cetuximab Plus Chemotherapy After First Progression in KRAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The UNICANCER PRODIGE18 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jan 1;5(1):83-90. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4465. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30422156 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: updated overall survival and molecular subgroup analyses of the open-label, phase 3 TRIBE study.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Oct;16(13):1306-15. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00122-9. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Lancet Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26338525 Clinical Trial.
-
Explaining the unexplainable: discrepancies in results from the CALGB/SWOG 80405 and FIRE-3 studies.Lancet Oncol. 2019 May;20(5):e274-e283. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30172-X. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31044725 Review.
-
Adenosine and adenosine receptors in colorectal cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Oct;87:106853. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106853. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32755765 Review.
Cited by
-
CD73 polymorphisms are associated with schizophrenia.Purinergic Signal. 2024 May 17. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-10004-3. Online ahead of print. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38758511
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Oct 7;6(1):362. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00670-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34620838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Variants of ANGPT1, CD39, FGF2 and MMP9 Linked to Clinical Outcome of Bevacizumab Plus Chemotherapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 30;22(3):1381. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031381. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33573134 Free PMC article.
-
The adenosine pathway in immuno-oncology.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Oct;17(10):611-629. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0382-2. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32514148 Review.
-
Germline variability and tumor expression level of ribosomal protein gene RPL28 are associated with survival of metastatic colorectal cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 10;9(1):13008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49477-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31506518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hausler SF, Montalban del Barrio I, Strohschein J, et al. Ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 on OvCA cells are potent adenosine-generating enzymes responsible for adenosine receptor 2A-dependent suppression of T cell function and NK cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2011; 60:1405–18. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Resta R, Yamashita Y, Thompson LF. Ecto-enzyme and signaling functions of lymphocyte CD73. Immunol Rev 1998; 161:95–109. - PubMed
-
- Yegutkin GG. Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: Important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008; 1783:673–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

