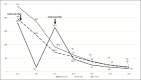
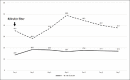
Hepatitis A Virus-induced Severe Hemolysis Complicated by Severe Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
- PMID: 30294135
- PMCID: PMC6161574
- DOI: 10.4103/ijccm.IJCCM_260_18
Hepatitis A Virus-induced Severe Hemolysis Complicated by Severe Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Abstract
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency is an x-linked recessive genetic disorder with mutation in the G6PD gene. Defect in the enzyme G6PD causes red blood cells (RBCs) to breakdown prematurely causing hemolytic anemia. Hemolytic anemia is also a known hematological complication associated with viral hepatitis. In such patients, hemolysis may be more severe if there is any secondary injury to RBC in the form of membrane defect, oxidative stress, or enzyme deficiency like in G6PD deficiency. Here, we present a case of an adult, not previously diagnosed with G6PD deficiency, who presented with viral hepatitis, severe hemolysis, and multiorgan failure.
Keywords: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; hemolytic anemia; hemoperfusion; hepatitis A; methemoglobinemia; multiorgan failure.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Syncope Following Treatment of UTI: A Case of Acute Hemolytic Anemia, Methemoglobinemia and Acute Renal Dysfunction Following Phenazopyridine Use in a Patient With G6PD Deficiency.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2023 Jan 10;13(1):54-57. doi: 10.55729/2000-9666.1144. eCollection 2023. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2023. PMID: 36817304 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Revealing Severe Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (G6PD-D) Deficiency with Methemoglobinemia: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2019 May 22;20:726-729. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.915007. Am J Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31113928 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Possible Link Between Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency, and Methemoglobinemia.Cureus. 2024 Jun 4;16(6):e61656. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61656. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38966448 Free PMC article.
-
Review and drug therapy implications of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018 Feb 1;75(3):97-104. doi: 10.2146/ajhp160961. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29305344 Review.
-
Rasburicase Therapy and G6PD and CYB5R Genotype.2020 Sep 29. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ, editors. Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012–. 2020 Sep 29. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ, editors. Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012–. PMID: 32997466 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Acute hepatitis A virus infection presenting with direct antiglobulin test-negative autoimmune hemolytic anemia and α-thalassemia trait.F1000Res. 2025 Apr 15;13:1224. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.156586.2. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2025. PMID: 40443430 Free PMC article.
-
Current investigations on clinical pharmacology and therapeutics of Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jun;222:107788. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107788. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33326820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scrub Typhus Infection Precipitating Hemolysis in a Patient With G6PD Deficiency: A Case Report.Clin Case Rep. 2025 Jan 24;13(2):e70142. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.70142. eCollection 2025 Feb. Clin Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39868405 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency among the fulminant hepatitis A virus infection patients.Caspian J Intern Med. 2024 Summer;15(3):451-458. doi: 10.22088/cjim.15.3.451. Caspian J Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 39011425 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Hepatitis A Causing Severe Hemolysis and Renal Failure in Undiagnosed Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficient Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Case Reports Hepatol. 2021 Jun 3;2021:5512883. doi: 10.1155/2021/5512883. eCollection 2021. Case Reports Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34188961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cappellini MD, Fiorelli G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Lancet. 2008;371:64–74. - PubMed
-
- Frank JE. Diagnosis and management of G6PD deficiency. Am Fam Physician. 2005;72:1277–82. - PubMed
-
- Luzzatto L, Nannelli C, Notaro R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2016;30:373–93. - PubMed
-
- Manganelli G, Masullo U, Passarelli S, Filosa S. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: Disadvantages and possible benefits. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2013;13:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Nkhoma ET, Poole C, Vannappagari V, Hall SA, Beutler E. The global prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2009;42:267–78. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous