Genomic Characterization and Probiotic Potency of Bacillus sp. DU-106, a Highly Effective Producer of L-Lactic Acid Isolated From Fermented Yogurt
- PMID: 30294310
- PMCID: PMC6158304
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02216
Genomic Characterization and Probiotic Potency of Bacillus sp. DU-106, a Highly Effective Producer of L-Lactic Acid Isolated From Fermented Yogurt
Abstract
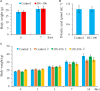
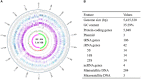
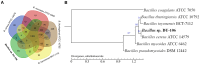
Bacillus sp. DU-106, a newly isolated member of Bacillus cereus group, exhibits the predominant ability to produce L-lactic acid. The probiotic potency of test strain revealed its survivability at acidic pH, bile salts and viability in simulated gastric juice in vitro. The acute oral toxicity test indicated its no toxicity to laboratory mice in vivo. We further determined the complete genome of strain DU-106 to understand genetic basis as a potential probiotic. It has a circular chromosome and three plasmids for a total genome 5,758,208 bp in size with a G + C content of 35.10%. Genes associated with lactate synthesis were found in the DU-106 genome. We also annotated various stress-related, bile salt resistance, and adhesion-related domains in this strain, which likely provide support in exerting probiotic action by enabling adhesion to host epithelial cells and survival under gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, strain DU-106 genome lacks the virulence genes encodes cereulide synthetase, enterotoxin FM, and cytotoxin K. These phenotypic and genomic probiotic potencies facilitate its potential candidate as probiotic starter in food industry.
Keywords: Bacillus sp. DU-106; complete genome sequence; lactic acid; probiotics; virulence gene.
Figures


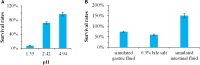
Similar articles
-
Functional Annotation Genome Unravels Potential Probiotic Bacillus velezensis Strain KMU01 from Traditional Korean Fermented Kimchi.Foods. 2021 Mar 9;10(3):563. doi: 10.3390/foods10030563. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33803098 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence and In Vitro Probiotic Assessment of Bacillus subtilis DC-11 Isolated from Traditionally Fermented Idli Batter.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Dec 10;82(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-04014-y. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39656272
-
Complete genome sequence of Bacillus coagulans CACC834 isolated from canine.J Anim Sci Technol. 2021 Nov;63(6):1464-1467. doi: 10.5187/jast.2021.e108. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Anim Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34957459 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted toxin profile, an approach toward a better understanding of probiotic Bacillus cereus.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019 Apr;49(4):342-356. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2019.1609410. Epub 2019 May 22. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31116061 Review.
-
In vitro selection criteria for probiotic bacteria of human origin: correlation with in vivo findings.Am J Clin Nutr. 2001 Feb;73(2 Suppl):386S-392S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/73.2.386s. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11157346 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and in-depth genome analysis of a halotolerant probiotic bacterium Paenibacillus sp. S-12, a multifarious bacterium isolated from Rauvolfia serpentina.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Jul 18;23(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02939-1. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37464310 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Activity and Plant Growth-Promoting Properties of Bacillus mojovensis B1302 against Rhizoctonia Cerealis.Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 20;10(8):1682. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081682. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36014099 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic-, phenotypic-, and toxicity-based safety assessment and probiotic potency of Bacillus coagulans IDCC 1201 isolated from green malt.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 1;48(5-6):kuab026. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab026. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33904924 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus Species as Direct-Fed Microbial Antibiotic Alternatives for Monogastric Production.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023 Feb;15(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09909-5. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023. PMID: 35092567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncultured Microorganisms and Their Functions in the Fermentation Systems of Traditional Chinese Fermented Foods.Foods. 2023 Jul 13;12(14):2691. doi: 10.3390/foods12142691. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37509783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjakul S., Karnjanapratum S., Visessanguan W. (2018). Hydrolysed collagen from Lates calcarifer skin: its acute toxicity and impact on cell proliferation and collagen production of fibroblasts. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 53 1871–1879. 10.1111/ijfs.13772 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

