Avelumab, an IgG1 anti-PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Triggers NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity and Cytokine Production Against Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 30294328
- PMCID: PMC6159755
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02140
Avelumab, an IgG1 anti-PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Triggers NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity and Cytokine Production Against Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
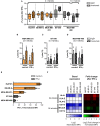
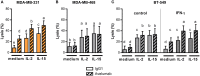
The standard treatment for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) patients is cytotoxic chemotherapy, but it is restricted since the duration of response is usually short. Blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway through monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) appears to be a promising therapeutic strategy for TNBC patients. Avelumab is a human IgG1 anti-PD-L1 mAb being tested in clinical trials that may also trigger antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) against cancer cells as an additional antitumor activity. In the present work, we studied in vitro Avelumab-mediated ADCC against a panel of TNBC cells with different PD-L1 expression using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) or purified NK cells from healthy donors. We determined that Avelumab significantly enhanced NK-cell mediated cytotoxicity against TNBC cells and that tumor cells expressing higher levels of PD-L1 were more sensitive to Avelumab-mediated ADCC. IFN-γ treatment upregulated PD-L1 expression in tumor cells but had a variable impact on Avelumab-mediated ADCC, which could be related to the simultaneous effect of IFN-γ on the expression of NK cell ligands. Moreover, IL-2 and IL-15 stimulation of NK cells enhanced Avelumab-triggered cytokine production and degranulation along with increased lytic activity against tumor cells. Improving the treatment of TNBC remains still a considerable challenge. This in vitro study suggests that Avelumab-mediated ADCC, independently of the blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, could be a valuable mechanism for tumor cell elimination in TNBC. Avelumab combination with immunomodulators such as IL-15 or IL-2 could be taken into consideration to increase the therapeutic efficacy of Avelumab in TNBC.
Keywords: ADCC; Avelumab; IFN-γ; IL-15; IL-2; PD-L1; triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Activity of a Novel Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Avelumab (MSB0010718C) on Human Tumor Cells.Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 Oct;3(10):1148-1157. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0059. Epub 2015 May 26. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26014098 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced killing of chordoma cells by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity employing the novel anti-PD-L1 antibody avelumab.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):33498-511. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9256. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27172898 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of the peripheral immunome following multiple administrations of avelumab, a human IgG1 anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Feb 21;5:20. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0220-y. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28239472 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab: combining immune checkpoint inhibition and antibody-dependent cytotoxicity.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017 Apr;17(4):515-523. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2017.1294156. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28274143 Review.
-
Checkpoint inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): Where to go from here.Cancer. 2018 May 15;124(10):2086-2103. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31272. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29424936 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting innate immunity for cancer immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Nov 27;22(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01885-w. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38008741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of NK cells with chimeric-switch receptors to overcome PD1-mediated inhibition in cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 May;72(5):1153-1167. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03317-y. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36355079 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting DNA Damage Response and Immune Checkpoint for Anticancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 17;23(6):3238. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063238. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modern Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 10;14(16):3860. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163860. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jul 6;22(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01805-y. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37415164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

