Therapeutic activity of sour orange albedo extract and abundant flavanones loaded silica nanoparticles against acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 30294554
- PMCID: PMC6170219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.08.021
Therapeutic activity of sour orange albedo extract and abundant flavanones loaded silica nanoparticles against acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity
Abstract
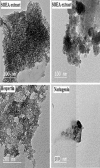
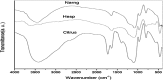
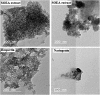
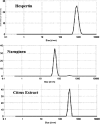
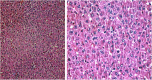
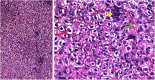
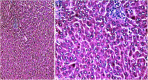
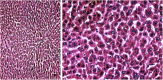
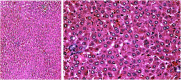
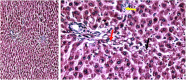
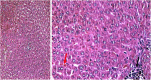
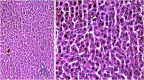
The current research aims to demonstrate the therapeutic effect of sour orange albedo extract (SOAE) and two flavanones loaded-tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) using sol-gel technique, in adose100 mg/kg body weight taken orally or45 days against acrylamide (ACR)toxicity in rats. This was achieved through measuring the activities of specific biochemical parameters related to liver functions in tissue of ACR intoxicated rats as compared to normal one. Liver functions included alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, antioxidants and oxidative stress biomarkers; superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione and lipid peroxide (malondialdehyde, MDA). Moreover, histological examination of liver was performed to confirm the biochemical findings. The present results clearly indicated disturbances in all biochemical parameters, such as increase in the liver function enzyme activities and MDA level. Results of ATPase enzyme activities revealed significant decrease in ACR intoxicated rats and liver biomarker enzymes declared significant decrease. On the other hand, treatment of intoxicated rats with the previous different nano-particles natural product demonstrated improvement in all biochemical parameters under investigation.
Keywords: Flavanones, acrylamide; Histopathology; Liver biochemical parameters; Nanocomposites; Sour orange albedo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The protection of Thymus vulgaris leaves alcoholic extract against hepatotoxicity of alcohol in rats.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017 Apr;10(4):361-371. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.03.023. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017. PMID: 28552106
-
Ellagic Acid Prevents Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Histopathological Alterations in Acrylamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Wistar Rats.J Diet Suppl. 2020;17(6):651-662. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2019.1634175. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Diet Suppl. 2020. PMID: 31342809
-
Protective effects of thymoquinone against acrylamide-induced liver, kidney and brain oxidative damage in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Oct;27(30):37709-37717. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09516-3. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32608003
-
Influence of ferulic acid consumption in ameliorating the cadmium-induced liver and renal oxidative damage in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jul;26(20):20631-20653. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05420-7. Epub 2019 May 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31104231
-
Protective effects of germinated and fermented soybean extract against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells and in rats.Food Funct. 2015 Nov;6(11):3512-21. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00785b. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 26299642
Cited by
-
Natural combination of phenolic glycosides from fruits resists pro-oxidant insults to colon cells and enhances intrinsic antioxidant status in mice.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Jul 18;6:703-711. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.07.005. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31372348 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition and studying the possible neuroprotective effect of iridoids-rich fraction from Pentas lanceolata leaves using rotenone model of Parkinson's disease in mice.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Dec;32(6):3953-3971. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01509-9. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38963536 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation of N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide-induced DNA destruction in the testis of adult rats by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and conditional medium.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 14;10(23):e40380. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40380. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39669145 Free PMC article.
-
Genus Sophora: a comprehensive review on secondary chemical metabolites and their biological aspects from past achievements to future perspectives.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 Nov;44(11):903-986. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01354-2. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34907492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hepatoprotective effect of livergol microemulsion preparation (nanoparticle) against bromobenzene induced toxicity in mice.Toxicol Rep. 2019 May 9;6:444-448. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.05.005. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31193476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Revathi S., Vuyyuru M., Dhanaraju M.D. Carbon nanotube: a flexible approach for nanomedicine and drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015;8:125–131.
-
- Wong B.S., Yoong S.L., Jagusiak A., Panczyk T., Ho H.K., Ang Pastorin W.H. Carbon nanotubes for delivery of small molecule drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013;65:1964–2015. - PubMed
-
- Taghizadehghalehjoughi A., Hacimuftuoglu A., Cetin M., Ugur A.B., Galateanu B., Mezhuev Y., Okkay U., Taspinar N., Taspinar M., Uyanik A., Gundogdu B., Mohammadzadeh M., Nalci K.A., Stivaktakis P., Tsatsakis A., Jung T.W., Jeong J.H., Abd El-Aty A.M. Effect of metformin/irinotecan-loaded poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles on glioblastoma:in vitro and in vivo studies. Nanomedicine. 2018;13:1595–1606. - PubMed
-
- Kuskova A.N., Kulikova P.P., Goryachayaa A.V., Tzatzarakisb M.N., Doceac A.O., Veloniad K., Shtilmana M.I., Tsatsakisb A.M. Amphiphilic poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles as carriers for non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs: in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo acute toxicity study. Nanomedicine. 2017;3:1021–1030. - PubMed
-
- I.C. Radu, A. Hudita, C. Zaharia1, P. O. Stanescu1, E. Vasile, H. Iovu, M. Stan, O. Ginghina, B. Galateanu, M. Costache, P. Langguth, A. Tsatsakis, K.Velonia, C. Negrei, Poly Hydroxy Butyrate-co-HydroxyValerate) (PHBHV) Nanocarriers for Silymarin Release as Adjuvant Therapy in Colo-rectal Cancer, Frontiers in Pharmacology. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

