Endosomal microautophagy is an integrated part of the autophagic response to amino acid starvation
- PMID: 30295124
- PMCID: PMC6287684
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1532265
Endosomal microautophagy is an integrated part of the autophagic response to amino acid starvation
Abstract
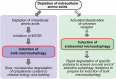
Starvation is a fundamental type of stress naturally occurring in biological systems. All organisms have therefore evolved different safeguard mechanisms to cope with deficiencies in various types of nutrients. Cells, from yeast to humans, typically respond to amino acid starvation by initiating degradation of cellular components by inducing autophagy. This degradation releases metabolic building blocks to sustain essential core cellular processes. Increasing evidence indicates that starvation-induced autophagy also acts to prepare cells for prolonged starvation by degrading key regulators of different cellular processes. In a recent study, we found that within the first hours of amino acid starvation cells elicit an autophagic response causing rapid degradation of specific proteins. The response is executed independently of both MTOR and canonical macroautophagy. Based on RNAi-mediated knockdown of essential components of the Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport (ESCRT) machinery and electron microscopy we conclude that the response relies on some sort of endosomal microautophagy, hence vesicle budding into endosomes. Substantiated by the different substrates that are selectively degraded by this novel pathway we propose that the response predominantly acts to prepare cells for prolonged starvation. Intriguingly, this includes shutting down selective macroautophagy in preparation for a massive induction of bulk macroautophagy.
Keywords: Amino acid starvation; MTOR; autophagy receptors; endosomal microautophagy; macroautophagy; selective autophagy.
Figures
Comment on
-
Starvation induces rapid degradation of selective autophagy receptors by endosomal microautophagy.J Cell Biol. 2018 Oct 1;217(10):3640-3655. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201711002. Epub 2018 Jul 17. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30018090 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous