Integrative genomic analysis reveals novel regulatory mechanisms of eyeless during Drosophila eye development
- PMID: 30295802
- PMCID: PMC6294497
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky892
Integrative genomic analysis reveals novel regulatory mechanisms of eyeless during Drosophila eye development
Abstract
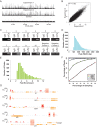
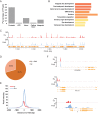
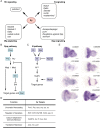
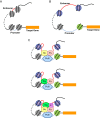
Eyeless (ey) is one of the most critical transcription factors for initiating the entire eye development in Drosophila. However, the molecular mechanisms through which Ey regulates target genes and pathways have not been characterized at the genomic level. Using ChIP-Seq, we generated an endogenous Ey-binding profile in Drosophila developing eyes. We found that Ey binding occurred more frequently at promoter compared to non-promoter regions. Ey promoter binding was correlated with the active transcription of genes involved in development and transcription regulation. An integrative analysis revealed that Ey directly regulated a broad and highly connected genetic network, including many essential patterning pathways, and known and novel eye genes. Interestingly, we observed that Ey could target multiple components of the same pathway, which might enhance its control of these pathways during eye development. In addition to protein-coding genes, we discovered Ey also targeted non-coding RNAs, which represents a new regulatory mechanism employed by Ey. These findings suggest that Ey could use multiple molecular mechanisms to regulate target gene expression and pathway function, which might enable Ey to exhibit a greater flexibility in controlling different processes during eye development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional divergence between eyeless and twin of eyeless in Drosophila melanogaster.Development. 2004 Aug;131(16):3943-53. doi: 10.1242/dev.01278. Epub 2004 Jul 14. Development. 2004. PMID: 15253940
-
twin of eyeless, a second Pax-6 gene of Drosophila, acts upstream of eyeless in the control of eye development.Mol Cell. 1999 Mar;3(3):297-307. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80457-8. Mol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10198632
-
Hipk promotes photoreceptor differentiation through the repression of Twin of eyeless and Eyeless expression.Dev Biol. 2014 Jun 1;390(1):14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.02.024. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24631217
-
NOTCH and the patterning of ommatidial founder cells in the developing Drosophila eye.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;37:35-58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-45398-7_4. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002. PMID: 25707068 Review. No abstract available.
-
Conservation and non-conservation of genetic pathways in eye specification.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):743-53. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041877ad. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558467 Review.
Cited by
-
The timing of cell fate decisions is crucial for initiating pattern formation in the Drosophila eye.Development. 2022 Jan 15;149(2):dev199634. doi: 10.1242/dev.199634. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Development. 2022. PMID: 35072208 Free PMC article.
-
A shared ancient enhancer element differentially regulates the bric-a-brac tandem gene duplicates in the developing Drosophila leg.PLoS Genet. 2022 Mar 16;18(3):e1010083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010083. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35294439 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in Pleiotropic Hub Gene Expression Is Associated with Interspecific Differences in Head Shape and Eye Size in Drosophila.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 May 4;38(5):1924-1942. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa335. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33386848 Free PMC article.
-
Accessible chromatin reveals regulatory mechanisms underlying cell fate decisions during early embryogenesis.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 12;11(1):7896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86919-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33846424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halder G., Callaerts P., Gehring W.J.. Induction of ectopic eyes by targeted expression of the eyeless gene in Drosophila. Science. 1995; 267:1788–1792. - PubMed
-
- Lindsley D.L., Zimm G.G.. The Genome of Drosophila Melanogaster. 1992; San Diego: Academic Press.
-
- Halder G., Callaerts P., Flister S., Walldorf U., Kloter U., Gehring W.J.. Eyeless initiates the expression of both sine oculis and eyes absent during Drosophila compound eye development. Development. 1998; 125:2181–2191. - PubMed
-
- Ton C.C., Hirvonen H., Miwa H., Weil M.M., Monaghan P., Jordan T., van Heyningen V., Hastie N.D., Meijers-Heijboer H., Drechsler M. et al. . Positional cloning and characterization of a paired box- and homeobox-containing gene from the aniridia region. Cell. 1991; 67:1059–1074. - PubMed
-
- Martin P., Carriere C., Dozier C., Quatannens B., Mirabel M.A., Vandenbunder B., Stehelin D., Saule S.. Characterization of a paired box- and homeobox-containing quail gene (Pax-QNR) expressed in the neuroretina. Oncogene. 1992; 7:1721–1728. - PubMed

