Differential regulation of PD-L1 expression by immune and tumor cells in NSCLC and the response to treatment with atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1)
- PMID: 30297397
- PMCID: PMC6205493
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1802166115
Differential regulation of PD-L1 expression by immune and tumor cells in NSCLC and the response to treatment with atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1)
Abstract
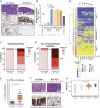
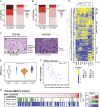
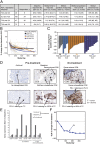
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression on tumor cells (TCs) by immunohistochemistry is rapidly gaining importance as a diagnostic for the selection or stratification of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) most likely to respond to single-agent checkpoint inhibitors. However, at least two distinct patterns of PD-L1 expression have been observed with potential biological and clinical relevance in NSCLC: expression on TC or on tumor-infiltrating immune cells (ICs). We investigated the molecular and cellular characteristics associated with PD-L1 expression in these distinct cell compartments in 4,549 cases of NSCLC. PD-L1 expression on IC was more prevalent and likely reflected IFN-γ-induced adaptive regulation accompanied by increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and effector T cells. High PD-L1 expression on TC, however, reflected an epigenetic dysregulation of the PD-L1 gene and was associated with a distinct histology described by poor immune infiltration, sclerotic/desmoplastic stroma, and mesenchymal molecular features. Importantly, durable clinical responses to atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1) were observed in patients with tumors expressing high PD-L1 levels on either TC alone [40% objective response rate (ORR)] or IC alone (22% ORR). Thus, PD-L1 expression on TC or IC can independently attenuate anticancer immunity and emphasizes the functional importance of IC in regulating the antitumor T cell response.
Keywords: PD-1; PD-L1; atezolizumab; cancer immunotherapy; checkpoints.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M. Kowanetz, W.Z., H.K., E.E.K., D.S., Z.B., N.M., S.F., V.L., D.S.S., M.B., S.M., G.S., R.F., G.H., A. Sandler, L.A., I.M., D.S.C., and P.S.H. are full-time employees of Genentech, which supported the research described and markets the therapeutic antibody atezolizumab, under study.
Figures

References
-
- Genentech, Inc. (2017) Tecentriq (atezolizumab) package insert (Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA)
-
- Merck & Co, Inc. (2017) Keytruda (pembrolizumab) package insert (Merck & Co, Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ)
-
- Bristol-Myers Squibb (2017) Opdivo (nivolumab) package insert (Bristol-Myers Squibb, New York)
-
- Reck M, et al. KEYNOTE-024 Investigators Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1823–1833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

