Chemical Components and Biological Activities of the Genus Phyllanthus: A Review of the Recent Literature
- PMID: 30297661
- PMCID: PMC6222918
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102567
Chemical Components and Biological Activities of the Genus Phyllanthus: A Review of the Recent Literature
Abstract
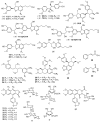
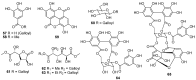
Medicinal plants have served humans since prehistoric times to treat various ailments. Both developed and underdeveloped countries rely on traditional systems of medication using natural sources from plants. Phyllanthus is one of the largest genus in the family Phyllanthaceae, comprising over 700 well known species cosmopolitan in distribution mainly in the tropics and subtropics. Phyllanthus species are being in constant used in traditional medications to cure an array of human diseases (constipation, inhalation related, arthritis, loss of appetite, injuries, conjunctivitis, diarrhoea, running nose, common cold, malaria, blennorrhagia, colic, diabetes mellitus, dysentery, indigestion, fever, gout, gonorrheal diseases of males and females, skin itching, jaundice, hepatic disorders, leucorrhea, vaginitis, menstrual irregularities, obesity, stomach pains, and tumors), confectionaries, food industry, and in some pesticides. Phyllanthus species are rich in diversity of phytochemicals e.g., tannins, terpenes, alkaloids, glycosidic compounds, saponins, and flavones etc. More in depth studies are a direly needed to identify more compounds with specific cellular functions to treat various ailments.
Keywords: Phyllanthus; biological activities; phytochemicals; traditional medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Haque T., Muhsin M.D.A., Akhter T., Haq M.E., Begum R., Chowdhury S.F.U.A. Antimicrobial and analgesic activity of leaf extracts of Phyllanthus reticulatus Poir. (Family-Euphorbiaceae) Jahangirnagar Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2016;5:81–85. doi: 10.3329/jujbs.v5i1.29746. - DOI
-
- Aboelsoud N.H. Herbal medicine in ancient Egypt. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010;4:82–86.
-
- Gismondi A., D’Agostino A., Canuti L., Di Marco G., Martínez-Labarga C., Angle M., Rickard O., Canini A. Dental calculus reveals diet habits and medicinal plant use in the Early Medieval Italian population of Colonna. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018;20:556–564. doi: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2018.05.023. - DOI
-
- Manjula V., Norman T.S.J. Phyllanthus reticulatus for oral health. J. Med. Plants. 2017;5:117–119.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources