Salt, water and nephron: Mechanisms of action and link to hypertension and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 30298656
- PMCID: PMC6221012
- DOI: 10.1111/nep.13465
Salt, water and nephron: Mechanisms of action and link to hypertension and chronic kidney disease
Abstract
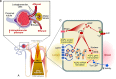
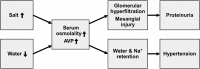
Our knowledge on sodium and water homeostasis and regulation continues to evolve. A considerable amount of new information in this area has emerged in recent years. This review summarizes existing and new literature and discusses complex multi-organ effects of high-salt and low-water intake and role of arginine vasopressin in this process, as well as the potential clinical significance of non-osmotic sodium storage pool and rhythmicity of urine sodium excretion. It has become clear that sodium and water dysregulation can exert profound effects on kidney and vascular health, far greater than previously recognized. Maladaptation to a combined high-salt and low-water intake can be linked to the growing epidemic of hypertension and chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: arginine vasopressin (AVP); chronic kidney disease (CKD); hypertension; non-osmotic pool of sodium; salt and water regulation; skin.
© 2018 The Authors Nephrology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Asian Pacific Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Christ‐Crain M, Fenske W. Copeptin in the diagnosis of vasopressin‐dependent disorders of fluid homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016; 12: 168–76. - PubMed
-
- Torres VE. Vasopressin receptor antagonists, heart failure, and polycystic kidney disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015; 66: 195–210. - PubMed
-
- Morgenthaler NG, Struck J, Alonso C, Bergmann A. Assay for the measurement of copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the precursor of vasopressin. Clin. Chem. 2006; 52: 112–9. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari SS, Loke I, Davies JE, Squire IB, Struck J, Ng LL. Gender and renal function influence plasma levels of copeptin in healthy individuals. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2009; 116: 257–63. - PubMed
-
- Gizowski C, Zaelzer C, Bourque CW. Clock‐driven vasopressin neurotransmission mediates anticipatory thirst prior to sleep. Nature 2016; 537: 685–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

