Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals common regulatory mechanisms between effector- and PAMP-triggered immunity in plants
- PMID: 30300945
- PMCID: PMC6367033
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.15523
Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals common regulatory mechanisms between effector- and PAMP-triggered immunity in plants
Abstract
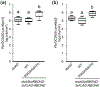
Plant immunity consists of two arms: pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI), induced by surface-localized receptors, and effector-triggered immunity (ETI), induced by intracellular receptors. Despite the little structural similarity, both receptor types activate similar responses with different dynamics. To better understand phosphorylation events during ETI, we employed a phosphoproteomic screen using an inducible expression system of the bacterial effector avrRpt2 in Arabidopsis thaliana, and identified 109 differentially phosphorylated residues of membrane-associated proteins on activation of the intracellular RPS2 receptor. Interestingly, several RPS2-regulated phosphosites overlap with sites that are regulated during PTI, suggesting that these phosphosites may be convergent points of both signaling arms. Moreover, some of these sites are residues of important defense components, including the NADPH oxidase RBOHD, ABC-transporter PEN3, calcium-ATPase ACA8, noncanonical Gα protein XLG2 and H+ -ATPases. In particular, we found that S343 and S347 of RBOHD are common phosphorylation targets during PTI and ETI. Our mutational analyses showed that these sites are required for the production of reactive oxygen species during both PTI and ETI, and immunity against avirulent bacteria and a virulent necrotrophic fungus. We provide, for the first time, large-scale phosphoproteomic data of ETI, thereby suggesting crucial roles of common phosphosites in plant immunity.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; bacteria; effectors; fungi; pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs); plant immunity; protein phosphorylation; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
© 2018 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2018 New Phytologist Trust.
Figures







Comment in
-
Convergence of cell-surface and intracellular immune receptor signalling.New Phytol. 2019 Mar;221(4):1676-1678. doi: 10.1111/nph.15634. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 30729583 No abstract available.
References
-
- Benschop JJ, Mohammed S, O’Flaherty M, Heck AJ, Slijper M, Menke FL. 2007. Quantitative phosphoproteomics of early elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(7): 1198–1214. - PubMed
-
- Boutrot F, Zipfel C. 2017. Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55: 257–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- BIO2015-64077-R/Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad of Spain/International
- RO1GM092772/National Institute of Health/International
- USDA-NIFA 2015-67013-23082/US Department of Agriculture/International
- JP16KT0037/MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI/International
- The Gatsby Charitable Foundation/International
- JP15H05959/MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI/International
- JP17H06172/MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI/International
- Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO)/International
- JP16H06186/MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI/International
- R01 GM092772/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- JP16J0071/MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI/International
- ERC_/European Research Council/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

