[Ultrasound-guided selective nerve blocks for trigger finger surgeries to maintain flexion/extension of fingers - Case series]
- PMID: 30301613
- PMCID: PMC9391729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjan.2018.06.011
[Ultrasound-guided selective nerve blocks for trigger finger surgeries to maintain flexion/extension of fingers - Case series]
Abstract
Background: A patient's ability to move his/her fingers during hand surgery may be helpful to surgeons because it allows the effectiveness of the intervention evaluation and prediction of hand function in the postoperative period. The purpose of this case series is to demonstrate the efficacy of an ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block technique to maintain the hand flexor and extensor muscles motor function and discuss the benefits of the technique for trigger finger surgery.
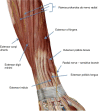
Case report: Ten patients scheduled to undergo trigger finger surgery were selected. The goal was to maintain flexion and extension of the fingers during the procedure. Thus, ultrasound-guided ulnar, radial, and medial nerve block was performed in the distal third of the forearm, at 5–7 cm proximal to the wrist. The block was performed with 5 mL of 0.375% bupivacaine on each nerve. All procedures were uneventfully performed maintaining the flexion and extension of the fingers. In two cases, it was observed that the motricity maintenance and the patients’ ability to move their fingers when requested allowed the success of the surgical procedure after the third intraoperative evaluation.
Conclusion: This case series shows that it is possible to maintain the motor function of the hand flexor and extensor muscles to perform finger trigger surgeries using specific ultrasound-guided distal blocks.
Keywords: Bloqueios seletivos; Flexion and extension of the fingers; Flexão e extensão dos dedos; Liberação dedo em gatilho; Selective nerve blocks; Trigger finger release; Ultrasound; Ultrassom.
Copyright © 2018. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Figures

References
-
- Lalonde D.H. Wide-awake flexor tendon repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123:623–625. - PubMed
-
- Lalonde D.H., Wong A. Dosage of local anesthesia in wide awake hand surgery. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38:2025–2028. - PubMed
-
- Hutting K., van Rappard J.R., Prins A., et al. Digital necrosis after local anaesthesia with epinephrine. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2015;159:9477. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

