IL-17 integrates multiple self-reinforcing, feed-forward mechanisms through the RNA binding protein Arid5a
- PMID: 30301788
- PMCID: PMC6188668
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aat4617
IL-17 integrates multiple self-reinforcing, feed-forward mechanisms through the RNA binding protein Arid5a
Abstract
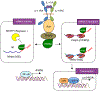
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) not only stimulates immunity to fungal pathogens but also contributes to autoimmune pathology. IL-17 is only a modest activator of transcription in experimental tissue culture settings. However, IL-17 controls posttranscriptional events that enhance the expression of target mRNAs. Here, we showed that the RNA binding protein (RBP) Arid5a (AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5a) integrated multiple IL-17-driven signaling pathways through posttranscriptional control of mRNA. IL-17 induced expression of Arid5a, which was recruited to the adaptor TRAF2. Arid5a stabilized IL-17-induced cytokine transcripts by binding to their 3' untranslated regions and also counteracted mRNA degradation mediated by the endoribonuclease MCPIP1 (Regnase-1). Arid5a inducibly associated with the eukaryotic translation initiation complex and facilitated the translation of the transcription factors (TFs) IκBζ (Nfkbiz ) and C/EBPβ (Cebpb). These TFs in turn transactivated IL-17-dependent promoters. Together, these data indicated that Arid5a orchestrates a feed-forward amplification loop, which promoted IL-17 signaling by controlling mRNA stability and translation.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
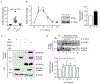
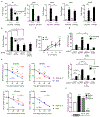
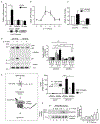
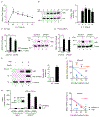
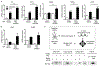
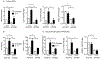
Comment in
-
Arid5a makes the IL-17A/F-responsive pathway less arid.Sci Signal. 2018 Oct 9;11(551):eaau8876. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aau8876. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 30301789
References
-
- Cua DJ, Tato CM, Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10, 479–489 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

