Peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates exhibiting pyrimidine-X cleavage specificity efficiently silence miRNA target acting synergistically with RNase H
- PMID: 30302012
- PMCID: PMC6177439
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33331-z
Peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates exhibiting pyrimidine-X cleavage specificity efficiently silence miRNA target acting synergistically with RNase H
Abstract
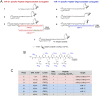
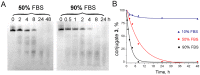
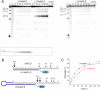
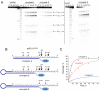
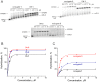
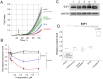
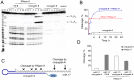
Taking into account the important role of miRNA in carcinogenesis, oncogenic miRNAs are attractive molecules for gene-targeted therapy. Here, we developed a novel series of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates exhibiting ribonuclease activity targeted to highly oncogenic miRNAs miR-21 and miR-17. When designing the conjugates, we enhanced both nuclease resistance of the targeted oligodeoxyribonucleotide by introducing at its 3'-end mini-hairpin structure displaying high thermostability and robustness against nuclease digestion and the efficiency of its functioning by attachment of the catalytic construction (amide)NH2-Gly(ArgLeu)4-TCAA displaying ribonuclease activity to its 5'-end. Designed miRNases efficiently cleaved miRNA targets, exhibiting Pyr-X specificity, and cleavage specificity had strong dependence on the miRNA sequence in the site of peptide location. In vitro, designed miRNases do not prevent cleavage of miRNA bound with the conjugate by RNase H, and more than an 11-fold enhancement of miRNA cleavage by the conjugate is observed in the presence of RNase H. In murine melanoma cells, miRNase silences mmu-miR-17 with very high efficiency as a result of miR-17 cleavage by miRNase and by recruited RNase H. Thus, miRNases provide a system of double attack of the miRNA molecules, significantly increasing the efficiency of miRNA downregulation in the cells in comparison with antisense oligonucleotide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual miRNases for Triple Incision of miRNA Target: Design Concept and Catalytic Performance.Molecules. 2020 May 25;25(10):2459. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102459. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32466298 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Selective Artificial Ribonucleases: Renaissance of Oligonucleotide Conjugates for Irreversible Cleavage of RNA Sequences.Molecules. 2021 Mar 19;26(6):1732. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061732. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33808835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalytic Knockdown of miR-21 by Artificial Ribonuclease: Biological Performance in Tumor Model.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 8;10:879. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00879. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31456683 Free PMC article.
-
miRNases: Novel peptide-oligonucleotide bioconjugates that silence miR-21 in lymphosarcoma cells.Biomaterials. 2017 Apr;122:163-178. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28126663
-
A comprehensive review on oncogenic miRNAs in breast cancer.J Genet. 2021;100:15. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 33764337 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual miRNases for Triple Incision of miRNA Target: Design Concept and Catalytic Performance.Molecules. 2020 May 25;25(10):2459. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102459. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32466298 Free PMC article.
-
Sry-related High Mobility Group Box 17 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Antagonizing the Wingless-related Integration Site Pathway.J Cancer Prev. 2020 Dec 30;25(4):204-212. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2020.25.4.204. J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 33409253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Trisbenzimidazole Phosphoramidite Building Block Enables High-Yielding Syntheses of RNA-Cleaving Oligonucleotide Conjugates.Molecules. 2020 Apr 16;25(8):1842. doi: 10.3390/molecules25081842. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32316292 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting non-coding RNA family members with artificial endonuclease XNAzymes.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 24;5(1):1010. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03987-5. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36153384 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Selective Artificial Ribonucleases: Renaissance of Oligonucleotide Conjugates for Irreversible Cleavage of RNA Sequences.Molecules. 2021 Mar 19;26(6):1732. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061732. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33808835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

