Chemical composition, antioxidant potential, macromolecule damage and neuroprotective activity of Convolvulus pluricaulis
- PMID: 30302329
- PMCID: PMC6174265
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.11.002
Chemical composition, antioxidant potential, macromolecule damage and neuroprotective activity of Convolvulus pluricaulis
Erratum in
-
Erratum for previously published articles.J Tradit Complement Med. 2020 Sep 28;10(6):605. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.09.001. eCollection 2020 Nov. J Tradit Complement Med. 2020. PMID: 33134138 Free PMC article.
Abstract
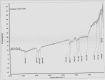
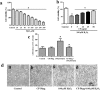
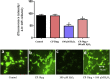
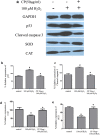
Herbal medicines are known to mitigate radical induced cell damage. Hence identification and scientific validation of herbal medicines contribute to better use in Ayurvedic/Unani research. In the present study, we investigated antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties of Convolvulus pluricaulis (C. pluricaulis). C. pluricaulis exhibited antioxidant potential evident by free radical scavenging activities. C. pluricaulis pretreatment inhibited H2O2 induced macromolecule damage such as plasmid DNA damage and AAPH induced oxidation of bovine serum albumin and lipid peroxidation of rat hepatic tissues. Further to identify the neuroprotective properties of C. pluricaulis, SHSY5Y cells were treated with H2O2 with or without pretreatment of C. pluricaulis. The C. pluricaulis pretreatment at 50 μg/ml dose exhibited 50% cell survival against 100 μM H2O2 challenge for 24 h and it also decreased the lactate dehydrogenase leakage. Further C. pluricaulis pretreatment restored and regulated the antioxidant and apoptosis markers such as SOD, CAT, p53, and caspase-3 and inhibited, reactive oxygen species generation and depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane. C. pluricaulis possess a high content of flavonoids and polyphenols and GC-MS and FTIR analysis showed a wide variety of compounds which may contribute to the observed effects.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Convolvulus pluricaulis; FTIR; GC-MS; Neuroprotection; SH-SY5Y.
Figures



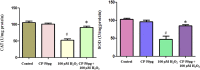



References
-
- Halliwell B. Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases. Drugs Aging. 2001;18:685–716. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P., Jha A.B., Dubey R.S., Pessarakli M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot. 2012;24:2012.
-
- Pande D., Negi R., Khanna R.S., Khanna H.D. Protein damage and antioxidant status alterations caused by oxidative injury in chronic myeloid leukemia. Einstein J Biol Medicine. 2016;27:55–58.
-
- Selvaraju V., Joshi M., Suresh S., Sanchez J.A., Maulik N., Maulik G. Diabetes, oxidative stress, molecular mechanism, and cardiovascular disease–an overview. Toxicol Mech Meth. 2012;22:330–335. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
