Phrenic nerve stimulation to treat patients with central sleep apnoea and heart failure
- PMID: 30303611
- PMCID: PMC6607512
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.1312
Phrenic nerve stimulation to treat patients with central sleep apnoea and heart failure
Abstract
Aims: The presence of central sleep apnoea (CSA) is associated with poor prognosis in patients with heart failure (HF). The aim of this analysis was to evaluate if using phrenic nerve stimulation to treat CSA in patients with CSA and HF was associated with changes in HF-specific metrics.
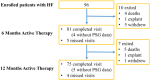
Methods and results: All patients randomized in the remedē System Pivotal Trial and identified at baseline with HF were included (n = 96). Effectiveness data from treatment and former control groups were pooled based on months since therapy activation. Changes from baseline to 6 and 12 months in sleep metrics, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, patient global assessment health-related quality of life, Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ), and echocardiographic parameters are reported. HF hospitalization, cardiovascular death, and the composite of HF hospitalization or cardiovascular death within 6 months are reported by the original randomized group assignment for safety assessment. Sleep metrics and quality of life improved from baseline to 6 and 12 months. At 12 months, MLHFQ scores changed by -6.8 ± 20.0 (P = 0.005). The 6-month rate of HF hospitalization was 4.7% in treatment patients (standard error = 3.3) and 17.0% in control patients (standard error = 5.5) (P = 0.065). Reported adverse events were as expected for a transvenous implantable system.
Conclusions: Phrenic nerve stimulation reduces CSA severity in patients with HF. In parallel, this CSA treatment was associated with benefits on HF quality of life.
Keywords: Central sleep apnoea; Heart failure; Phrenic nerve stimulation.
© 2018 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Treating central sleep apnoea in heart failure: is pull better than push?Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Dec;20(12):1755-1759. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1337. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 30350905 No abstract available.
References
-
- Javaheri S, Parker TJ, Liming JD, Corbett WS, Nishiyama H, Wexler L, Roselle GA. Sleep apnea in 81 ambulatory male patients with stable heart failure. Types and their prevalences, consequences, and presentations. Circulation 1998;97:2154–2159. - PubMed
-
- Javaheri S, Shukla R, Zeigler H, Wexler L. Central sleep apnea, right ventricular dysfunction, and low diastolic blood pressure are predictors of mortality in systolic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49:2028–2034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

