Tissue Expander Complications Do Not Preclude a Second Successful Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction
- PMID: 30303927
- PMCID: PMC6310090
- DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005131
Tissue Expander Complications Do Not Preclude a Second Successful Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
Background: Implant-based breast reconstruction is the most common method of breast reconstruction in the United States, but the outcomes of subsequent implant-based reconstruction after a tissue expander complication are rarely studied. The purpose of this study was to determine the long-term incidence of implant loss in patents with a previous tissue expander complication.
Methods: This is a retrospective review of the long-term outcomes of all patients with tissue expander complications at a large academic medical center from 2003 to 2013. Patients with subsequent tissue expander or implant complications were compared to those with no further complications to assess risk factors for additional complications or reconstructive failure.
Results: One hundred sixty-two women were included in this study. The mean follow-up period was 8.3 ± 3.1 years. Forty-eight women (30 percent) went on to undergo a second tissue expander or implant placement. They did not differ from women who went on to autologous reconstruction or no further reconstruction. Of these, 34 women (71 percent) had no further complications and 38 women (79 percent) had a successful implant-based reconstruction at final follow-up. There were no patient or surgical factors significantly associated with a second complication or implant loss.
Conclusions: Following tissue expander complications, it is reasonable to offer women a second attempt at tissue expansion and implant placement. This study demonstrates that long-term success rates are high, and there are no definitive patient or surgical factors that preclude a second attempt at implant-based breast reconstruction.
Clinical question/level of evidence: Risk, III.
Figures


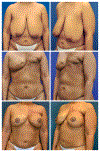
Comment in
-
Discussion: Tissue Expander Complications Do Not Preclude a Second Successful Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Jan;143(1):35-36. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005170. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019. PMID: 30589772 No abstract available.
-
Tissue Expander Complications Do Not Preclude a Second Successful Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Nov;144(5):936e-937e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006126. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019. PMID: 31425419 No abstract available.
-
Reply: Tissue Expander Complications Do Not Preclude a Second Successful Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Nov;144(5):937e-938e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006127. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019. PMID: 31425421 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic Surgery Statistics Reprot 2016. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2016/plastic-su.... Accessed January 21, 2018.
-
- Tsoi B, Ziolkowski NI, Thoma A, Campbell K, O’Reilly D, Goeree R. Safety of tissue expander/implant versus autologous abdominal tissue breast reconstruction in postmastectomy breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg February 2014;133(2):234–249. - PubMed
-
- Spear SL, Newman MK, Bedford MS, Schwartz KA, Cohen M, Schwartz JS. A retrospective analysis of outcomes using three common methods for immediate breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg August 2008;122(2):340–347. - PubMed
-
- Alderman AK, Wilkins EG, Kim HM, Lowery JC. Complications in postmastectomy breast reconstruction: two-year results of the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcome Study. Plast Reconstr Surg June 2002;109(7):2265–2274. - PubMed
-
- Spear SL, Masden D, Rao SS, Nahabedian MY. Long-term outcomes of failed prosthetic breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg September 2013;71(3):286–291. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

