Atomic force microscopy reveals new biophysical markers for monitoring subcellular changes in oxidative injury: Neuroprotective effects of quercetin at the nanoscale
- PMID: 30303965
- PMCID: PMC6179194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200119
Atomic force microscopy reveals new biophysical markers for monitoring subcellular changes in oxidative injury: Neuroprotective effects of quercetin at the nanoscale
Erratum in
-
Correction: Atomic force microscopy reveals new biophysical markers for monitoring subcellular changes in oxidative injury: Neuroprotective effects of quercetin at the nanoscale.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 6;14(2):e0212150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212150. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30726293 Free PMC article.
Abstract
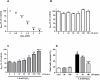
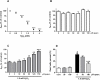
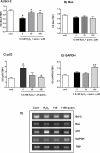
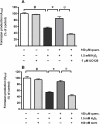
Oxidative stress has been recognised as an important pathological mechanism underlying the development of neurodegenerative diseases. The biomarkers for assessing the degree of oxidative stress have been attracting much interest because of their potential clinical relevance in understanding the cellular effects of free radicals and evaluation of the efficacy of drug treatment. Here, an interdisciplinary approach using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and cellular and biological molecular methods were used to investigate oxidative damage in P19 neurons and to reveal the underlying mechanism of protective action of quercetin. Biological methods demonstrated the oxidative damage of P19 neurons and showed that quercetin improved neuronal survival by preventing H2O2-induced p53 and Bcl-2 down-regulation and modulated Akt and ERK1/2 signalling pathways. For the first time, AFM was employed to evaluate morphologically (roughness, height, Feret dimension) and nanomechanical (elasticity) properties in H2O2-induced neuronal damage. The AFM analysis revealed that quercetin suppressed H2O2-provoked changes in cell membrane elasticity and morphological properties, thus confirming its neuroprotective activity. The obtained results indicate the potential of AFM-measured parameters as a biophysical markers of oxidative stress-induced neurodegeneration. In general, our study suggests that AFM can be used as a highly valuable tool in other biomedical applications aimed at screening and monitoring of drug-induced effects at cellular level.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

