N-dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone influences the levels of thiol and proteins related to oxidation-reduction process in Salmonella
- PMID: 30304064
- PMCID: PMC6179229
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204673
N-dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone influences the levels of thiol and proteins related to oxidation-reduction process in Salmonella
Abstract
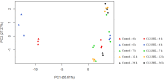
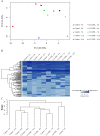
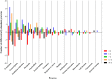
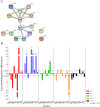
Quorum sensing is a cell-cell communication mechanism mediated by chemical signals that leads to differential gene expression in response to high population density. Salmonella is unable to synthesize the autoinducer-1 (AI-1), N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL), but is able to recognize AHLs produced by other microorganisms through SdiA protein. This study aimed to evaluate the fatty acid and protein profiles of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis PT4 578 throughout time of cultivation in the presence of AHL. The presence of N-dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone (C12-HSL) altered the fatty acid and protein profiles of Salmonella cultivated during 4, 6, 7, 12 and 36 h in anaerobic condition. The profiles of Salmonella Enteritidis at logarithmic phase of growth (4 h of cultivation), in the presence of C12-HSL, were similar to those of cells at late stationary phase (36 h). In addition, there was less variation in both protein and fatty acid profiles along growth, suggesting that this quorum sensing signal anticipated a stationary phase response. The presence of C12-HSL increased the abundance of thiol related proteins such as Tpx, Q7CR42, Q8ZP25, YfgD, AhpC, NfsB, YdhD and TrxA, as well as the levels of free cellular thiol after 6 h of cultivation, suggesting that these cells have greater potential to resist oxidative stress. Additionally, the LuxS protein which synthesizes the AI-2 signaling molecule was differentially abundant in the presence of C12-HSL. The NfsB protein had its abundance increased in the presence of C12-HSL at all evaluated times, which is a suggestion that the cells may be susceptible to the action of nitrofurans or that AHLs present some toxicity. Overall, the presence of C12-HSL altered important pathways related to oxidative stress and stationary phase response in Salmonella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Quecán BXV, Rivera MLC, Pinto UM. Bioactive phytochemicals targeting microbial activities mediated by quorum sensing In: Kalia V, editor. Biotechnological applications of quorum sensing inhibitors. Singapore: Springer; 2018. pp.397–416.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

