Cryotherapy: biochemical alterations involved in reduction of damage induced by exhaustive exercise
- PMID: 30304134
- PMCID: PMC6172926
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X20187702
Cryotherapy: biochemical alterations involved in reduction of damage induced by exhaustive exercise
Abstract
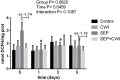
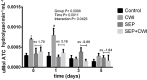
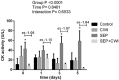
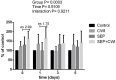
When exercises are done in intense or exhaustive modes, several acute biochemical mechanisms are triggered. The use of cryotherapy as cold-water immersion is largely used to accelerate the process of muscular recovery based on its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. The present study aimed to study the biochemical effects of cold-water immersion treatment in mice submitted to exercise-induced exhaustion. Swiss albino mice were divided into 4 treatment groups: control, cold-water immersion (CWI), swimming exhaustive protocol (SEP), and SEP+CWI. Treatment groups were subdivided into times of analysis: 0, 1, 3, and 5 days. Exhaustion groups were submitted to one SEP session, and the CWI groups submitted to one immersion session (12 min at 12°C) every 24 h. Reactive species production, inflammatory, cell viability, and antioxidant status were assessed. The SEP+CWI group showed a decrease in inflammatory damage biomarkers, and reactive species production, and presented increased cell viability compared to the SEP group. Furthermore, CWI increased acetylcholinesterase activity in the first two sessions. The present study showed that CWI was an effective treatment after exercise-induced muscle damage. It enhanced anti-inflammatory response, decreased reactive species production, increased cell viability, and promoted redox balance, which could decrease the time for the recovery process.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cold water immersion or LED therapy after training sessions: effects on exercise-induced muscle damage and performance in rats.Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Jul;34(5):991-999. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2689-0. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30456534
-
Recovery From Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: Cold-Water Immersion Versus Whole-Body Cryotherapy.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2017 Mar;12(3):402-409. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2016-0186. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2017. PMID: 27396361 Clinical Trial.
-
Modulation of cardiac vascular endothelial growth factor and PGC-1α with regular postexercise cold-water immersion of rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Apr 1;126(4):1110-1116. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00918.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30676864
-
What are the Physiological Mechanisms for Post-Exercise Cold Water Immersion in the Recovery from Prolonged Endurance and Intermittent Exercise?Sports Med. 2016 Aug;46(8):1095-109. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0483-3. Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 26888646 Review.
-
What Parameters Influence the Effect of Cold-Water Immersion on Muscle Soreness? An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin J Sport Med. 2023 Jan 1;33(1):13-25. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000001081. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Clin J Sport Med. 2023. PMID: 36399666
Cited by
-
Comparison between cryotherapy and photobiomodulation in muscle recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Apr;37(3):1375-1388. doi: 10.1007/s10103-021-03442-7. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34669081
-
α-Klotho Expression in Mouse Tissues Following Acute Exhaustive Exercise.Front Physiol. 2019 Dec 10;10:1498. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01498. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31920703 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of electrophysical resources on healing of neurotendinous injury in an experimental model of type I diabetes and kidney disease.Acta Cir Bras. 2022 Jun 27;37(4):e370402. doi: 10.1590/acb370402. eCollection 2022. Acta Cir Bras. 2022. PMID: 35766669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McArdle WD, Katch FI, Katch VL. Exercise Physiology: energy, nutrition and human performance. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan; 2011. 7 ed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

