2'- O-Methyl-8-methylguanosine as a Z-Form RNA Stabilizer for Structural and Functional Study of Z-RNA
- PMID: 30304782
- PMCID: PMC6222775
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102572
2'- O-Methyl-8-methylguanosine as a Z-Form RNA Stabilizer for Structural and Functional Study of Z-RNA
Abstract
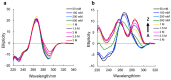
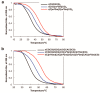
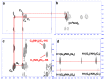
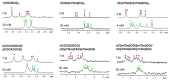
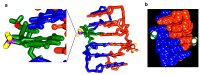
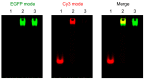
In contrast to Z-DNA that was stabilized and well-studied for its structure by chemical approaches, the stabilization and structural study of Z-RNA remains a challenge. In this study, we developed a Z-form RNA stabilizer m⁸Gm, and demonstrated that incorporation of m⁸Gm into RNA can markedly stabilize the Z-RNA at low salt conditions. Using the m⁸Gm-contained Z-RNA, we determined the structure of Z-RNA and investigated the interaction of protein and Z-RNA.
Keywords: NMR; Z-RNA structure; circular dichroism; synthesis of oligonucleotide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

