Genetic Characterization and Pathogenicity of a Novel Recombined Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 among Nadc30-Like, Jxa1-Like, and Mlv-Like Strains
- PMID: 30304818
- PMCID: PMC6213465
- DOI: 10.3390/v10100551
Genetic Characterization and Pathogenicity of a Novel Recombined Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 among Nadc30-Like, Jxa1-Like, and Mlv-Like Strains
Abstract
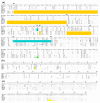
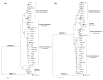
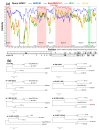
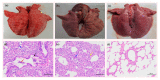
Recombination among porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses (PRRSVs), coupled with point mutations, insertions, and deletions occurring in the genome, is considered to contribute to the emergence of new variants. Here, we report the complete genome sequences of a PRRSV field strain, designated SCN17, isolated from a RespPRRS MLV-vaccinated piglet in China in 2017. Sequence alignment revealed that SCN17 had discontinuous 131-amino acid (111 + 1 + 19-aa) deletion in the NSP2-coding region identical to that of NADC30 when compared to VR-2332. Notably, the strain, SCN17, contained an additional 1-aa deletion in NSP2, a 1-aa deletion in ORF5, and a unique 3-nt deletion in the 3'-UTR. Phylogenetic analysis showed that SCN17 clustered into NADC30-like lineage based on ORF5 genotyping, whereas it belonged to an inter-lineage between the NADC30-like and VR-2332-like lineages as established based on the full-length genome. Importantly, the SCN17 was identified as a novel virus recombined between a NADC30-like (moderately pathogenic), a JXA1-like (highly pathogenic), and an attenuated vaccine strain, RespPRRS MLV (parental strain VR-2332). Furthermore, we tested its pathogenicity in piglets. SCN17 infection caused a persistent fever, moderate interstitial pneumonia, and increased the viremia and antibody levels in the inoculated piglets. Of note, all SCN17-infected piglets survived throughout the study. The new virus was showed to be a moderately virulent isolate and have lower pathogenicity than HP-PRRSV strain, SCwhn09CD. Our results provide evidence for the continuing evolution of PRRSV field strain by genetic recombination and mutation leading to outbreaks in the vaccinated pig populations in China.
Keywords: modified live virus (MLV); mutation; pathogenicity; porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV); recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Keffaber K. Reproductive failure of unknown etiology. Am. Assoc. Swine Pract. Newsl. 1989;1:1–9.
-
- Cavanagh D. Nidovirales: A new order comprising coronaviridae and arteriviridae. Arch. Virol. 1997;142:629–633. - PubMed
-
- Adams M.J., Lefkowitz E.J., King A.M.Q., Harrach B., Harrison R.L., Knowles N.J., Kropinski A.M., Krupovic M., Kuhn J.H., Mushegian A.R., et al. Changes to taxonomy and the international code of virus classification and nomenclature ratified by the international committee on taxonomy of viruses (2017) Arch. Virol. 2017;162:2505–2538. doi: 10.1007/s00705-017-3358-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benfield D.A., Nelson E., Collins J.E., Harris L., Goyal S.M., Robison D., Christianson W.T., Morrison R.B., Gorcyca D., Chladek D. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332) J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1992;4:127–133. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400202. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018JY0640/the Applied Basic Research Program of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province/International
- 2018NZZJ008/the Transformation of Agricultural Achievements in Sichuan Province/International
- 2018NZDZX0006/the Major Science and Technology Projects in Sichuan Province/International
- SASA2017A07/the Public Welfare Scientific Research Institutes Basic Research Projects/International
- 2018YSZH0005/the Transformation Fund of Scientific and Technological Achievements of Scientific Research Institutes in Sichuan Province/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

