Chitosan-Based In Situ Gels for Ocular Delivery of Therapeutics: A State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 30304825
- PMCID: PMC6212818
- DOI: 10.3390/md16100373
Chitosan-Based In Situ Gels for Ocular Delivery of Therapeutics: A State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
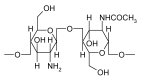
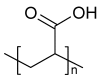
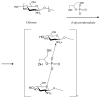
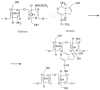
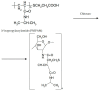
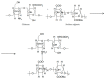
Ocular in situ gels are a promising alternative to overcome drawbacks of conventional eye drops because they associate the advantages of solutions such as accuracy and reproducibility of dosing, or ease of administration with prolonged contact time of ointments. Chitosan is a natural polymer suitable for use in ophthalmic formulations due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, mucoadhesive character, antibacterial and antifungal properties, permeation enhancement and corneal wound healing effects. The combination of chitosan, pH-sensitive polymer, with other stimuli-responsive polymers leads to increased mechanical strength of formulations and an improved therapeutic effect due to prolonged ocular contact time. This review describes in situ gelling systems resulting from the association of chitosan with various stimuli-responsive polymers with emphasis on the mechanism of gel formation and application in ophthalmology. It also comprises the main techniques for evaluation of chitosan in situ gels, along with requirements of safety and ocular tolerability.
Keywords: chitosan; in situ gels; mucoadhesion; ocular delivery; sol–gel transition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
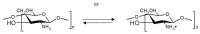
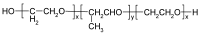
Similar articles
-
Enhancing and sustaining the topical ocular delivery of fluconazole using chitosan solution and poloxamer/chitosan in situ forming gel.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011 Oct;79(2):320-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.05.006. Epub 2011 May 27. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011. PMID: 21641994
-
Hybrid thermosensitive-mucoadhesive in situ forming gels for enhanced corneal wound healing effect of L-carnosine.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):374-385. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2023236. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35068268 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of ion-activated in situ gelling systems for ocular drug delivery. Part 1: physicochemical characterisation and in vitro release.Int J Pharm. 2011 Jun 15;411(1-2):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.03.042. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21453762
-
Poloxamer-based in situ gelling thermoresponsive systems for ocular drug delivery applications.Drug Discov Today. 2019 Aug;24(8):1575-1586. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.05.036. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Drug Discov Today. 2019. PMID: 31175956 Review.
-
Ocular application of chitosan.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012 Jun;9(6):701-12. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2012.681775. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012. PMID: 22530690 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Sedative Dexmedetomidine Sublingual In Situ Gels: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 18;14(2):220. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020220. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35213953 Free PMC article.
-
Biopolymers in Mucoadhesive Eye Drops for Treatment of Dry Eye and Allergic Conditions: Application and Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 31;15(2):470. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020470. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mapping of Antifungal Mechanisms Accessing Biomaterials and New Agents to Target Oral Candidiasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 7;23(14):7520. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147520. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formulation, Optimization and Evaluation of Luteolin-Loaded Topical Nanoparticulate Delivery System for the Skin Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 20;13(11):1749. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111749. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834164 Free PMC article.
-
Caspofungin-Loaded Formulations for Treating Ocular Infections Caused by Candida spp.Gels. 2023 Apr 20;9(4):348. doi: 10.3390/gels9040348. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37102960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mali M.N., Hajare A.A. In situ gel-forming systems for sustained ocular drug delivery. Eur. Ind. Pharm. 2010;5:17–20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

