Scabiosa Genus: A Rich Source of Bioactive Metabolites
- PMID: 30304864
- PMCID: PMC6313729
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines5040110
Scabiosa Genus: A Rich Source of Bioactive Metabolites
Abstract
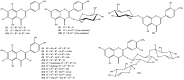
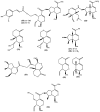
The genus Scabiosa (family Caprifoliaceae) is considered large (618 scientific plant names of species) although only 62 have accepted Latin binominal names. The majority of the Scabiosa species are widely distributed in the Mediterranean region and some Scabiosa species are used in traditional medicine systems. For instance, Scabiosa columbaria L. is used traditionally against diphtheria while S. comosa Fisch. Ex Roem. and Schult. is used in Mongolian and Tibetan traditional medical settings to treat liver diseases. The richness of Scabiosa species in secondary metabolites such as iridoids, flavonoids and pentacyclic triterpenoids may contribute to its use in folk medicine. Details on the most recent and relevant pharmacological in vivo studies on the bioactive secondary metabolites isolated from Scabiosa species will be summarized and thoroughly discussed.
Keywords: Scabiosa; anti-inflammatory; antibacterial; anticancer; antioxidant; flavonoids; iridoids; pentacyclic triterpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dipsacus and Scabiosa Species-The Source of Specialized Metabolites with High Biological Relevance: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Apr 27;28(9):3754. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093754. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-liver fibrosis effect of total flavonoids from Scabiosa comosa Fisch. ex Roem. et Schult. on liver fibrosis in rat models and its proteomics analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 Mar;9(2):272-285. doi: 10.21037/apm.2020.02.29. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32233617
-
Investigation of Phytochemical, Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potentials of Scabiosa L. (Caprifoliaceae) Species with Chemometric Methods.Chem Biodivers. 2024 Feb;21(2):e202301652. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202301652. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38240171
-
[To explore mechanism of Scabiosa comosa against liver fibrosis based on pharmacodynamics and network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jul;47(13):3609-3618. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220207.702. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35850815 Chinese.
-
The genus Nepeta: Traditional uses, phytochemicals and pharmacological properties.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113679. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113679. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33307050 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Potential and Medical Use of Secondary Metabolites.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Jun 12;6(2):66. doi: 10.3390/medicines6020066. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31212776 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Investigation of Phytochemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Scabiosa pseudograminifolia Hub.-Mor.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2025 May 14;22(2):104-118. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2025.12247. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40366211 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical compositions by using LC-MS/MS and GC-MS and antioxidant activities of methanolic extracts from leaf and flower parts of Scabiosa columbaria subsp. columbaria var. columbaria L.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Nov;28(11):6639-6644. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.039. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34764779 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of the Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Scabiosa atropurpurea subsp. maritima Fruit Extracts and Their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Properties.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 May 7;12(9):1585. doi: 10.3390/nano12091585. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35564294 Free PMC article.
-
Dipsacus and Scabiosa Species-The Source of Specialized Metabolites with High Biological Relevance: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Apr 27;28(9):3754. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093754. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lehbili M., Magid A.A., Hubert J., Kabouche A., Voutquenne-Nazabadioko L., Renault J.-H., Nuzillard J.-M., Morjani H., Abedini A., Gangloff S.C., et al. Two new bis-iridoids isolated from Scabiosa stellata and their antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase and cytotoxic activities. Fitoterapia. 2018;125:41–48. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2017.12.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The Plant List Database. [(accessed on 10 September 2018)]; Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Scabiosa.
-
- George E.B., Ronald J.T. Toxic Plants of North America. John Wiley and Sons; Oxford, UK: 2013. pp. 319–322.
-
- Carlson S.E., Linder P.H., Donoghue M.J. The historical biogeography of Scabiosa (dipsacaceae): Implications for Old World plant disjunctions. J. Biogeogr. 2012;39:1086–1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2011.02669.x. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

