Combination of berberine and ciprofloxacin reduces multi-resistant Salmonella strain biofilm formation by depressing mRNA expressions of luxS, rpoE, and ompR
- PMID: 30304890
- PMCID: PMC6265579
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.6.808
Combination of berberine and ciprofloxacin reduces multi-resistant Salmonella strain biofilm formation by depressing mRNA expressions of luxS, rpoE, and ompR
Abstract
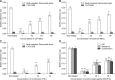
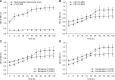
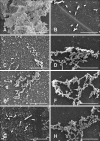
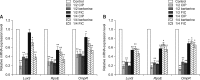
Bacterial biofilms have been demonstrated to be closely related to clinical infections and contribute to drug resistance. Berberine, which is the main component of Coptis chinensis, has been reported to have efficient antibacterial activity. This study aimed to investigate the potential effect of a combination of berberine with ciprofloxacin (CIP) to inhibit Salmonella biofilm formation and its effect on expressions of related genes (rpoE, luxS, and ompR). The fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index of the combination of berberine with CIP is 0.75 showing a synergistic antibacterial effect. The biofilm's adhesion rate and growth curve showed that the multi-resistant Salmonella strain had the potential to form a biofilm relative to that of strain CVCC528, and the antibiofilm effects were in a dose-dependent manner. Biofilm microstructures were rarely observed at 1/2 × MIC/FIC concentrations (MIC, minimal inhibition concentration), and the combination had a stronger antibiofilm effect than each of the antimicrobial agents used alone at 1/4 × FIC concentration. LuxS, rpoE, and ompR mRNA expressions were significantly repressed (p < 0.01) at 1/2 × MIC/FIC concentrations, and the berberine and CIP combination repressed mRNA expressions more strongly at the 1/4 × FIC concentration. The results indicate that the combination of berberine and CIP has a synergistic effect and is effective in inhibiting Salmonella biofilm formation via repression of luxS, rpoE, and ompR mRNA expressions.
Keywords: Salmonella; berberine; biofilm; drug combinations; multidrug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Abdallah M, Benoliel C, Drider D, Dhulster P, Chihib NE. Biofilm formation and persistence on abiotic surfaces in the context of food and medical environments. Arch Microbiol. 2014;196:453–472. - PubMed
-
- Bai L, Zhao J, Gan X, Wang J, Zhang X, Cui S, Xia S, Hu Y, Yan S, Wang J, Li F, Fanning S, Xu J. Emergence and diversity of Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana isolates with concurrent resistance to ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime from patients and food-producing animals in China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60:3365–3371. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castelijn GA, Parabirsing JA, Zwietering MH, Moezelaar R, Abee T. Surface behaviour of S. Typhimurium, S. Derby, S. Brandenburg and S. Infantis. Vet Microbiol. 2013;161:305–314. - PubMed
-
- Castelijn GA, van der Veen S, Zwietering MH, Moezelaar R, Abee T. Diversity in biofilm formation and production of curli fimbriae and cellulose of Salmonella Typhimurium strains of different origin in high and low nutrient medium. Biofouling. 2012;28:51–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

