Protection against the overuse and underuse of health care - methodological considerations for establishing prioritization criteria and recommendations in general practice
- PMID: 30305090
- PMCID: PMC6180663
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-018-3569-9
Protection against the overuse and underuse of health care - methodological considerations for establishing prioritization criteria and recommendations in general practice
Abstract
Background: Initiatives such as "Choosing Wisely" in the USA and "Smarter Medicine" in Switzerland have published lists of widely overused health care services. The German initiative "Choosing Wisely Together (Gemeinsam Klug Entscheiden)" follows this example. The goal of our study was to prioritize important recommendations against the overuse and underuse of health care services. The final list of recommendations will be published in the German guideline "Protection against the overuse and underuse of health care".
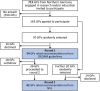
Methods: First, a multidisciplinary expert panel established a catalogue of prioritization criteria. Second, we extracted all the recommendations from evidence- and consensus-based German College of General Practice and Family Medicine (DEGAM) guidelines and National Health Care Guidelines (NVL). Third, the recommendations were rated by two independent panels (general practitioners and other health care professionals involved/not involved in guideline development). The prioritization process was finalized in a consensus conference held by DEGAM's Standing Guideline Committee (SLK).
Results: Eleven prioritization criteria were established. A total of 782 recommendations were extracted and rated by 98 physicians and other health care professionals in a survey. In the voting process, more than 80% of the recommendations were eliminated. After the final consensus conference, twelve recommendations from DEGAM guidelines, nine DEGAM addenda and 17 NVL recommendations were chosen for inclusion in the guideline, for a total of 38 recommendations.
Conclusion: The selection procedure proved helpful in identifying the highest priority recommendations with which to combat the overuse and underuse of health care services. To date, in Germany there has been no attempt to compile such a list by using a systematic and transparent methodology. Hence, the guideline that results from this process can fill an important gap.
Keywords: Clinical practice guidelines; Guideline development; Overuse; Primary care; Underuse.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
For the guideline development and for the final version of the paper no human subjects, human material, or human data were generated or used. On this account a formal ethics approval and a consent to participate were not required for this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Kadel C, Burger W, Klepzig H. Qualitätssicherung in der invasiven Kardiologie: Eine prospektive Untersuchung zur Bewertung von Indikationen zur Koronarangiographie und zur Koronardilatation nach der Methode der RAND Corporation. DMW - Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1996;121(15):465–471. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1043028. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

