Prepubertal skeletal muscle growth requires Pax7-expressing satellite cell-derived myonuclear contribution
- PMID: 30305290
- PMCID: PMC6215399
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.167197
Prepubertal skeletal muscle growth requires Pax7-expressing satellite cell-derived myonuclear contribution
Abstract
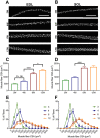
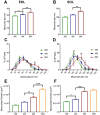
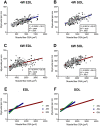
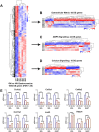
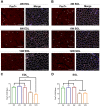
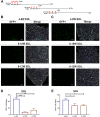
The functional role of Pax7-expressing satellite cells (SCs) in postnatal skeletal muscle development beyond weaning remains obscure. Therefore, the relevance of SCs during prepubertal growth, a period after weaning but prior to the onset of puberty, has not been examined. Here, we have characterized mouse skeletal muscle growth during prepuberty and found significant increases in myofiber cross-sectional area that correlated with SC-derived myonuclear number. Remarkably, genome-wide RNA-sequencing analysis established that post-weaning juvenile and early adolescent skeletal muscle have markedly different gene expression signatures. These distinctions are consistent with extensive skeletal muscle maturation during this essential, albeit brief, developmental phase. Indelible labeling of SCs with Pax7CreERT2/+ ; Rosa26nTnG/+ mice demonstrated SC-derived myonuclear contribution during prepuberty, with a substantial reduction at puberty onset. Prepubertal depletion of SCs in Pax7CreERT2/+ ; Rosa26DTA/+ mice reduced myofiber size and myonuclear number, and caused force generation deficits to a similar extent in both fast and slow-contracting muscles. Collectively, these data demonstrate SC-derived myonuclear accretion as a cellular mechanism that contributes to prepubertal hypertrophic skeletal muscle growth.
Keywords: Aging; Extracellular matrix; Hypertrophy; Mouse; Musculoskeletal; Pediatric; Postnatal growth; Regeneration; Stem cell.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Allen D. L., Roy R. R. and Edgerton V. R. (1999). Myonuclear domains in muscle adaptation and disease. Muscle Nerve 22, 1350-1360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

