SUMO protease SENP1 deSUMOylates and stabilizes c-Myc
- PMID: 30305424
- PMCID: PMC6205424
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1802932115
SUMO protease SENP1 deSUMOylates and stabilizes c-Myc
Abstract
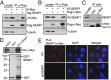
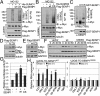
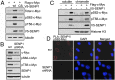
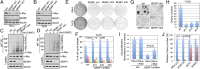
Posttranslational modifications play a crucial role in the proper control of c-Myc protein stability and activity. c-Myc can be modified by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO). However, how SUMOylation regulates c-Myc stability and activity remains to be elucidated. The deSUMOylation enzyme, SENP1, has recently been shown to have a prooncogenic role in cancer; however, mechanistic understanding of this is limited. Here we show that SENP1 is a c-Myc deSUMOylating enzyme. SENP1 interacts with and deSUMOylates c-Myc in cells and in vitro. Overexpression of wild-type SENP1, but not its catalytically inactive C603S mutant, markedly stabilizes c-Myc and increases its levels and activity. Knockdown of SENP1 reduces c-Myc levels, induces cell cycle arrest, and drastically suppresses cell proliferation. We further show that c-Myc can be comodified by both ubiquitination and SUMOylation. SENP1-mediated deSUMOylation reduces c-Myc polyubiquitination, suggesting that SUMOylation promotes c-Myc degradation through the proteasome system. Interestingly, SENP1-mediated deSUMOylation promotes the accumulation of monoubiquitinated c-Myc and its phosphorylation at serine 62 and threonine 58. SENP1 is frequently overexpressed, correlating with the high expression of c-Myc, in breast cancer tissues. Together, these results reveal that SENP1 is a crucial c-Myc deSUMOylating enzyme that positively regulates c-Myc's stability and activity.
Keywords: SENP1; SUMOylation; c-Myc; deSUMOylation; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kress TR, Sabò A, Amati B. MYC: Connecting selective transcriptional control to global RNA production. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:593–607. - PubMed
-
- Meyer N, Penn LZ. Reflecting on 25 years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:976–990. - PubMed
-
- Nesbit CE, Tersak JM, Prochownik EV. MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 1999;18:3004–3016. - PubMed
-
- Hann SR. Role of post-translational modifications in regulating c-Myc proteolysis, transcriptional activity and biological function. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:288–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

