Unintended intra-arterial injection of contrast of an intracranial CT angiography
- PMID: 30305864
- PMCID: PMC6175775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.09.005
Unintended intra-arterial injection of contrast of an intracranial CT angiography
Abstract
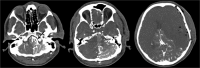
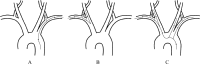
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) is widely used to evaluate intracranial vascular disease. We report a case of intracranial CTA with unintended intra-arterial (IA) injection of contrast due to IA placement of an intravenous cannula, which results in a selective left vertebral artery IA CTA. Knowledge of anatomy is essential in analyzing the whole study and identifying the error. In clinical practice, it is important to avoid and recognize a wrongly placed intravenous cannula. And bolus tracking protocol might play a role as a gatekeeper.
Keywords: Computed tomography angiography; Intra-arterial injection.
Figures

References
-
- Gandhi D. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography in cervicocranial vascular disease. J Neuroophthalmol. 2004;24(4):306–314. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi D, Pandey A, Ansari SA, Gemmete JJ, Thompson BJ, Mukherji SK. Multi-detector row CT angiography with direct intra-arterial contrast injection for the evaluation of neurovascular disease: technique, applications, and initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(5):1054–1058. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sen S, Chini EN, Brown MJ. Complications after unintentional intra-arterial injection of drugs: risks, outcomes, and management strategies. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80(6):783–795. - PubMed
-
- Devulapalli C, Han KD, Bello RJ, LaPorte DM, Hepper CT, Katz RD. Inadvertent intra-arterial drug injections in the upper extremity: systematic review. J Hand Surg Am. 2015;40(11):2262–2268. e5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

