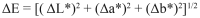Effect of different bleaching protocols on whitening efficiency and enamel superficial microhardness
- PMID: 30305875
- PMCID: PMC6174019
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.54967
Effect of different bleaching protocols on whitening efficiency and enamel superficial microhardness
Abstract
Background: Tooth bleaching is a popular aesthetic treatment to modify the color of teeth. Despite the extensive literature concerning the subject, there is still no consensus regarding the application mode of the different bleaching agents and their effect on enamel. Therefore, this study evaluated the influence of different bleaching protocols on whitening efficiency and enamel superficial hardness.
Material and methods: Bovine enamel fragments were embedded in acrylic resin and wet-sanded to obtain a flat buccal surface. The specimens were then randomly divided into 6 groups (n=10), based on the bleaching material [HP Maxx 35% (35% hydrogen peroxide), HP Blue 35% (35% hydrogen peroxide + Ca) and Whiteness Perfect 10% (10% carbamide peroxide)] and application mode (3 applications of 15 min, 1 application of 45 min, 1 application of 1h30 or 1 application of 3h30). The color and superficial hardness were assessed before and after bleaching. The color was assessed by means of a digital spectrophotometer, using CIELab parameters. Vickers hardness was determined using a load of 200g for 10s. Data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA with repeated measures and Tukey's test (α = 0.05).
Results: Concerning the color alteration, the groups were similar to each other, except for at-home bleaching protocols, which were statistically different from each other. Similarly, there was a reduction in hardness values comparing the initial and final periods, with lowest final hardness for the at-home bleaching protocol group applied for 3h30.
Conclusions: It can be concluded that the bleaching protocols influenced the final color and enamel surface hardness, evidencing that lower gel concentrations applied for longer periods promoted greater variation in color and lower final hardness. Key words:Tooth bleaching, roughness, microhardness, in-office, at-home bleaching.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that are no conflict of interest regarding this article. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Similar articles
-
Effect of different peroxide bleaching regimens and subsequent fluoridation on the hardness of human enamel and dentin.J Prosthet Dent. 2004 Oct;92(4):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2004.07.019. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. PMID: 15507905
-
Effect of bleaching agents on hardness, surface roughness and color parameters of dental enamel.J Clin Exp Dent. 2020 Jul 1;12(7):e670-e675. doi: 10.4317/jced.56913. eCollection 2020 Jul. J Clin Exp Dent. 2020. PMID: 32905007 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of in-office bleaching gels with calcium or fluoride on color, roughness, and enamel microhardness.J Clin Exp Dent. 2020 Feb 1;12(2):e116-e122. doi: 10.4317/jced.56006. eCollection 2020 Feb. J Clin Exp Dent. 2020. PMID: 32071692 Free PMC article.
-
Over-the-counter bleaching agents can help with tooth whitening maintenance.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2022 Mar;34(2):328-334. doi: 10.1111/jerd.12617. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2022. PMID: 32627389
-
Effect of bleaching agents on the hardness and morphology of enamel.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2002;14(1):24-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.2002.tb00144.x. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2002. PMID: 11915392
Cited by
-
Combination of strontium chloride and photobiomodulation in the control of tooth sensitivity post-bleaching: A split-mouth randomized clinical trial.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 28;16(4):e0250501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250501. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33909659 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dental enamel bleached for a prolonged and excessive time: Morphological changes.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 5;14(4):e0214948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214948. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30951549 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Measurements of the Depth of Enamel Demineralization before and after Bleach: An In Vitro Study.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 27;2022:2805343. doi: 10.1155/2022/2805343. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36065254 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a Self-Assembly Peptide on Surface Roughness and Hardness of Bleached Enamel.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Jun 13;13(2):79. doi: 10.3390/jfb13020079. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35735934 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative evaluation of the effect of three different concentrations of in-office bleaching agents on microhardness and surface roughness of enamel - An in vitro study.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2021 Jun 22;18:49. eCollection 2021. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2021. PMID: 34429869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Geus JL, Wambier LM, Kossatz S, Loguercio AD, Reis A. At-home vs In-office Bleaching: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Oper Dent. 2016;41:341–56. - PubMed
-
- Roderjan DA, Stanislawczuk R, Hebling J, Costa CA, Reis A, Loguercio AD. Response of human pulps to different in-office bleaching techniques: preliminary findings. Braz Dent J. 2015;26:242–8. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Gao J, Jiang T, Liang S, Zhou Y, Matis BA. Evaluation of the efficacy of potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride as desensitizing agents during tooth bleaching treatment—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2015;43:913–23. - PubMed
-
- Soares DG, Basso FG, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA. Concentrations of and application protocols for hydrogen peroxide bleaching gels: effects on pulp cell viability and whitening efficacy. J Dent. 2014;42:185–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous