Lysosome: The metabolic signaling hub
- PMID: 30306667
- PMCID: PMC6294686
- DOI: 10.1111/tra.12617
Lysosome: The metabolic signaling hub
Abstract
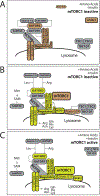
For the past five decades, the lysosome has been characterized as an unglamorous cellular recycling center. This notion has undergone a radical shift in the last 10 years, with new research revealing that this organelle serves as a major hub for metabolic signaling pathways. The discovery that master growth regulators, including the protein kinase mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin), make their home at the lysosomal surface has generated intense interest in the lysosome's key role in nutrient sensing and cellular homeostasis. The transcriptional networks required for lysosomal maintenance and function are just being unraveled and their connection to lysosome-based signaling pathways revealed. The catabolic and anabolic pathways that converge on the lysosome connect this organelle with multiple facets of cellular function; when these pathways are deregulated they underlie multiple human diseases, and promote cellular and organismal aging. Thus, understanding how lysosome-based signaling pathways function will not only illuminate the fascinating biology of this organelle but will also be critical in unlocking its therapeutic potentials.
Keywords: autophagy; lysosome; mTORC1; metabolic signaling.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
D.W.L has received funding from, and is a scientific advisory board member of, Aeonian Pharmaceuticals, which seeks to develop novel, selective mTOR inhibitors for the treatment of various diseases.
Figures
References
-
- de Duve C The lysosome turns fifty. Nat Cell Biol 2005;7(9):847–849. - PubMed
-
- Straus W Isolation and biochemical properties of droplets from the cells of rat kidney. J Biol Chem 1954;207(2):745–755. - PubMed
-
- Forgac M Vacuolar ATPases: rotary proton pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007;8(11):917–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

