Inhaled combination of sildenafil and rosiglitazone improves pulmonary hemodynamics, cardiac function, and arterial remodeling
- PMID: 30307312
- PMCID: PMC6383494
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00381.2018
Inhaled combination of sildenafil and rosiglitazone improves pulmonary hemodynamics, cardiac function, and arterial remodeling
Abstract
Currently, dual- or triple-drug combinations comprising different vasodilators are the mainstay for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). However, the patient outcome continues to be disappointing because the existing combination therapy cannot restrain progression of the disease. Previously, we have shown that when given as a monotherapy, long-acting inhaled formulations of sildenafil (a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor) and rosiglitazone (a peroxisome proliferator receptor-γ agonist) ameliorate PAH in rats. Thus, with a goal to develop a new combination therapy, we prepared and characterized poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)-based long-acting inhalable particles of sildenafil and rosiglitazone. We then assessed the efficacy of the combinations of sildenafil and rosiglitazone, given in plain forms or as PLGA particles, in reducing mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) and improving pulmonary arterial remodeling and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) in Sugen 5416 plus hypoxia-induced PAH rats. After intratracheal administration of the formulations, we catheterized the rats and measured mPAP, cardiac output, total pulmonary resistance, and RVH. We also conducted morphometric studies using lung tissue samples and assessed the degree of muscularization, the arterial medial wall thickening, and the extent of collagen deposition. Compared with the plain drugs, given via the pulmonary or oral route as a single or dual combination, PLGA particles of the drugs, although given at a longer dosing interval compared with the plain drugs, caused more pronounced reduction in mPAP without affecting mean systemic pressure, improved cardiac function, slowed down right heart remodeling, and reduced arterial muscularization. Overall, PLGA particles of sildenafil and rosiglitazone, given as an inhaled combination, could be a viable alternative to currently available vasodilator-based combination therapy for PAH.
Keywords: arterial remodeling; inhalation delivery; pulmonary arterial hypertension; right ventricular hypertrophy; rosiglitazone; sildenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures



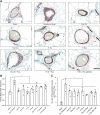
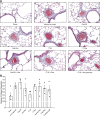
References
-
- Alzoubi A, Toba M, Abe K, O’Neill KD, Rocic P, Fagan KA, McMurtry IF, Oka M. Dehydroepiandrosterone restores right ventricular structure and function in rats with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304: H1708–H1718, 2013. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00746.2012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

