Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugates of Steric Blocking Oligonucleotides as Therapeutics for Neuromuscular Diseases from a Historical Perspective to Current Prospects of Treatment
- PMID: 30307373
- PMCID: PMC6386087
- DOI: 10.1089/nat.2018.0747
Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugates of Steric Blocking Oligonucleotides as Therapeutics for Neuromuscular Diseases from a Historical Perspective to Current Prospects of Treatment
Abstract
The review starts with a historical perspective of the achievements of the Gait group in synthesis of oligonucleotides (ONs) and their peptide conjugates toward the award of the 2017 Oligonucleotide Therapeutic Society Lifetime Achievement Award. This acts as a prelude to the rewarding collaborative studies in the Gait and Wood research groups aimed toward the enhanced delivery of charge neutral ON drugs and the development of a series of Arg-rich cell-penetrating peptides called Pip (peptide nucleic acid/phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligonucleotide [PNA/PMO] internalization peptides) as conjugates of such ONs. In this review we concentrate on these developments toward the treatment of the neuromuscular diseases Duchenne muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy toward a platform technology for the enhancement of cellular and in vivo delivery suitable for widespread use as neuromuscular and neurodegenerative ON drugs.
Keywords: conjugate; neuromuscular; oligonucleotide; peptide; therapeutic.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.G., M.J.A.W., and C.G. are cofounder shareholders of PepGen, a company dedicated to the peptide-based enhancement of delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotide analogs. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
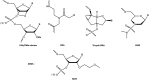
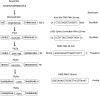

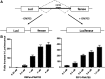
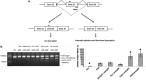
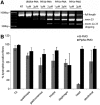
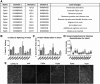
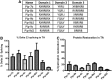
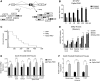
References
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Straub V, Hemmings R, Haas M, Schlosser-Weber G, Stoyanova-Beninska V, Mercuri E, Muntoni F, Sepodes B, Vroom E, Balabanov P. (2017). Development of exon skipping therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: a critical review and a perspective on the outstanding issues. Nucleic Acid Ther 27:251–259 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
